mirror of
https://github.com/zekexiao/pocketlang.git
synced 2025-02-05 20:26:53 +08:00
Merge pull request #35 from ThakeeNathees/readme-update
readme updated with performance benchmarks
This commit is contained in:
commit
39c3bb41a0
33
README.md
33
README.md
@ -1,14 +1,13 @@
|
||||
# PocketLang
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center" >
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/41085900/117528974-88fa8d00-aff2-11eb-8001-183c14786362.png" width="500" >
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
**PocketLang** is a small (~3000 semicollons) and fast programming language written in C. It's syntactically similar to Ruby and it can be learned in less than an hour. Including the compiler, bytecode VM and runtime, it's a standalone executable with zero external dependecies just as it's self descriptive name. The pocketlang VM can be embedded in another hosting program very easily, as static/shared library or a generated single header version of the source, which makes it even effortless.
|
||||
**Pocketlang** is a small (~3000 semicollons) and fast functional programming language written in C. It's syntactically similar to Ruby and it can be learned in less than an hour. Including the compiler, bytecode VM and runtime, it's a standalone executable with zero external dependecies just as it's self descriptive name. The pocketlang VM can be embedded in another hosting program very easily.
|
||||
|
||||
The language is written using [Wren Language](https://wren.io/) and their wonderful book [craftinginterpreters](http://www.craftinginterpreters.com/) as a reference.
|
||||
|
||||
### What PocketLang looks like
|
||||
### What pocketlang looks like
|
||||
|
||||
```ruby
|
||||
# Python like import statement.
|
||||
@ -26,3 +25,31 @@ for i in 0..10
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
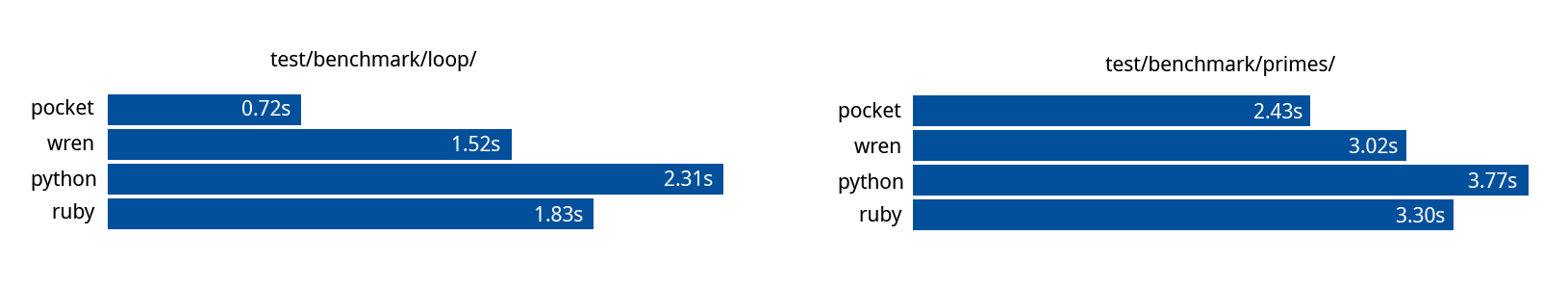
## Performance!
|
||||
|
||||
The source files used to run benchmarks could be found at `test/benchmarks/` directory. They were ran using a small python script in the test directory.
|
||||
- PC: ASUS N552VX, Intel Core i7-6700HQ 2.6GHz, 12GB SODIMM Ram
|
||||
- Lnaguages: pocketlang (pre-alpha), wren v0.3.0, python v3.7.4, ruby v2.7.2,
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
When it comes to loops pocketlang much faster (even faster than [wren](https://wren.io/), the language I'm using as a reference) because we have dedicated opcode instructions for iterations and calling builtin functions. And it's is a functional language, which makes is possible to avoid object orianted/ class instance creation overhead.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Building From Source
|
||||
|
||||
It can be build from source easily without any depencency, requirenments or even a build system, just a c99 compatible compiler is enough. It can be compiled with the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
#### gcc/mingw
|
||||
```
|
||||
gcc -o pocket cli/*.c src/*.c -Isrc/include -lm -Wno-int-to-pointer-cast
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### msvc
|
||||
```
|
||||
cl /Fepocket cli/*.c src/*.c /Isrc/include && rm *.obj
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For other compilers it's the same (If you weren't able to compile it, please report by [opening an issue](https://github.com/ThakeeNathees/pocketlang/issues/new)). In addition you can use some of our build scripts (Makefile, batch script for MSVC, SCons) in the `build/` directory. For more see [build from source docs](https://thakeenathees.github.io/pocketlang/Getting%20Started/build%20from%20source.html).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
42
src/core.c
42
src/core.c
@ -557,6 +557,37 @@ void stdMathCeil(PKVM* vm) {
|
||||
RET(VAR_NUM(ceil(num)));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void stdMathPow(PKVM* vm) {
|
||||
double num, ex;
|
||||
if (!validateNumeric(vm, ARG1, &num, "Parameter 1")) return;
|
||||
if (!validateNumeric(vm, ARG2, &ex, "Parameter 2")) return;
|
||||
|
||||
RET(VAR_NUM(pow(num, ex)));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void stdMathSqrt(PKVM* vm) {
|
||||
double num;
|
||||
if (!validateNumeric(vm, ARG1, &num, "Parameter 1")) return;
|
||||
|
||||
RET(VAR_NUM(sqrt(num)));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void stdMathAbs(PKVM* vm) {
|
||||
double num;
|
||||
if (!validateNumeric(vm, ARG1, &num, "Parameter 1")) return;
|
||||
if (num < 0) num = -num;
|
||||
RET(VAR_NUM(num));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void stdMathSign(PKVM* vm) {
|
||||
double num;
|
||||
if (!validateNumeric(vm, ARG1, &num, "Parameter 1")) return;
|
||||
if (num < 0) num = -1;
|
||||
else if (num > 0) num = +1;
|
||||
else num = 0;
|
||||
RET(VAR_NUM(num));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
PK_DOC(stdMathHash,
|
||||
"hash(value:var) -> num\n"
|
||||
"Return the hash value of the variable, if it's not hashable it'll "
|
||||
@ -623,6 +654,10 @@ void initializeCore(PKVM* vm) {
|
||||
Script* math = newModuleInternal(vm, "math");
|
||||
moduleAddFunctionInternal(vm, math, "floor", stdMathFloor, 1);
|
||||
moduleAddFunctionInternal(vm, math, "ceil", stdMathCeil, 1);
|
||||
moduleAddFunctionInternal(vm, math, "pow", stdMathPow, 2);
|
||||
moduleAddFunctionInternal(vm, math, "sqrt", stdMathSqrt, 1);
|
||||
moduleAddFunctionInternal(vm, math, "abs", stdMathAbs, 1);
|
||||
moduleAddFunctionInternal(vm, math, "sign", stdMathSign, 1);
|
||||
moduleAddFunctionInternal(vm, math, "hash", stdMathHash, 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -656,7 +691,12 @@ Var varAdd(PKVM* vm, Var v1, Var v2) {
|
||||
} break;
|
||||
|
||||
case OBJ_LIST:
|
||||
TODO;
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (o2->type == OBJ_LIST) {
|
||||
TODO;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
TODO;
|
||||
|
||||
case OBJ_MAP:
|
||||
case OBJ_RANGE:
|
||||
|
||||
18
src/var.c
18
src/var.c
@ -759,6 +759,24 @@ bool isValuesEqual(Var v1, Var v2) {
|
||||
memcmp(s1->data, s2->data, s1->length) == 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case OBJ_LIST: {
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* l1 = []; list_append(l1, l1) # [[...]]
|
||||
* l2 = []; list_append(l2, l2) # [[...]]
|
||||
* l1 == l2 ## This will cause a stack overflow but not handling that
|
||||
* ## (in python too).
|
||||
*/
|
||||
List *l1 = (List*)o1, *l2 = (List*)o2;
|
||||
if (l1->elements.count != l2->elements.count) return false;
|
||||
Var* v1 = l1->elements.data;
|
||||
Var* v2 = l2->elements.data;
|
||||
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < l1->elements.count; i++) {
|
||||
if (!isValuesEqual(*v1, *v2)) return false;
|
||||
v1++, v2++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,10 @@
|
||||
from lang import clock
|
||||
|
||||
start = clock()
|
||||
|
||||
N = 50000000; factors = []
|
||||
for i in 1..N+1
|
||||
if N % i == 0
|
||||
list_append(factors, i)
|
||||
end
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
print("elapsed:", clock() - start, 's')
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,8 +8,7 @@ end
|
||||
|
||||
start = clock()
|
||||
for i in 0..10
|
||||
print(fib(32))
|
||||
print(fib(30))
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
print('elapsed:', clock() - start, 's')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,5 +6,5 @@ def fib(n):
|
||||
|
||||
start = clock()
|
||||
for i in range(0, 10):
|
||||
print(fib(32))
|
||||
print(fib(30))
|
||||
print("elapsed: ", clock() - start, 's')
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,6 +9,6 @@ end
|
||||
|
||||
start = Time.now
|
||||
for i in 0...10
|
||||
puts fib(32)
|
||||
puts fib(30)
|
||||
end
|
||||
puts "elapsed: " + (Time.now - start).to_s + ' s'
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Fib {
|
||||
static get(n) {
|
||||
if (n < 2) return n
|
||||
@ -9,6 +8,6 @@ class Fib {
|
||||
|
||||
var start = System.clock
|
||||
for (i in 0...10) {
|
||||
System.print(Fib.get(32))
|
||||
System.print(Fib.get(30))
|
||||
}
|
||||
System.print("elapsed: %(System.clock - start)")
|
||||
System.print("elapsed: %(System.clock - start) s")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,10 +13,8 @@ def reverse_list(list)
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
start = clock()
|
||||
|
||||
N = 20000000
|
||||
l = (0..N).as_list
|
||||
reverse_list(l)
|
||||
|
||||
print(clock() - start, 's')
|
||||
print('elapsed: ', clock() - start, 's')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,4 +12,4 @@ start = clock()
|
||||
N = 20000000
|
||||
l = list(range(N))
|
||||
reverse_list(l)
|
||||
print(clock() - start, 's')
|
||||
print('elapsed: ', clock() - start, 's')
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,15 +1,10 @@
|
||||
from lang import clock
|
||||
|
||||
start = clock()
|
||||
|
||||
list = []
|
||||
for i in 0..10000000
|
||||
list_append(list, i)
|
||||
end
|
||||
l = []
|
||||
for i in 0..10000000 do list_append(l, i) end
|
||||
sum = 0
|
||||
for i in list
|
||||
sum += i
|
||||
end
|
||||
for i in l do sum += i end
|
||||
print(sum)
|
||||
|
||||
print("elapsed:", clock() - start)
|
||||
print("elapsed:", clock() - start, 's')
|
||||
|
||||
@ -7,4 +7,4 @@ var sum = 0
|
||||
for (i in list) sum = sum + i
|
||||
System.print(sum)
|
||||
|
||||
System.print("elapsed: %(System.clock - start)")
|
||||
System.print("elapsed: %(System.clock - start) s")
|
||||
@ -9,8 +9,7 @@ def is_prime(n)
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
start = clock()
|
||||
|
||||
N = 60000; primes = []
|
||||
N = 30000; primes = []
|
||||
for i in 0..N
|
||||
if is_prime(i)
|
||||
list_append(primes, i)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ def is_prime(n):
|
||||
|
||||
start = clock()
|
||||
|
||||
N = 60000; primes = []
|
||||
N = 30000; primes = []
|
||||
for i in range(N):
|
||||
if is_prime(i):
|
||||
primes.append(i)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ def is_prime(n)
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
start = Time.now
|
||||
N = 60000; primes = []
|
||||
N = 30000; primes = []
|
||||
for i in 0...N
|
||||
if is_prime(i)
|
||||
primes.append(i)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,12 +9,12 @@ var is_prime = Fn.new {|n|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
var start = System.clock
|
||||
var N = 60000
|
||||
var N = 30000
|
||||
var primes = []
|
||||
for (i in 0...N) {
|
||||
if (is_prime.call(i)) {
|
||||
primes.add(i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
System.print("elapsed: %(System.clock - start)")
|
||||
System.print("elapsed: %(System.clock - start) s")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,18 +1,16 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## Fib test.
|
||||
|
||||
res = ''
|
||||
## Iterative fibonacci function.
|
||||
|
||||
def fib(n)
|
||||
res = []
|
||||
a = 0; b = 1
|
||||
for _ in 0..n
|
||||
res += to_string(a) + " "
|
||||
temp = a;
|
||||
a = b;
|
||||
b += temp;
|
||||
list_append(res, a)
|
||||
temp = a; a = b; b += temp;
|
||||
end
|
||||
return res
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
fib(10)
|
||||
print(res)
|
||||
assert(res == '0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 ')
|
||||
fibs = fib(10)
|
||||
print('fibs =', fibs)
|
||||
assert(fibs == [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34])
|
||||
|
||||
9
test/examples/fizzbuzz.pk
Normal file
9
test/examples/fizzbuzz.pk
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for i in 1..100
|
||||
if i%3 == 0 and i%5 == 0 then print('fizzbuzz')
|
||||
elif i%3 == 0 then print('fizz')
|
||||
elif i%5 == 0 then print('buzz')
|
||||
else print(i)
|
||||
end
|
||||
end
|
||||
1
test/examples/helloworld.pk
Normal file
1
test/examples/helloworld.pk
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
print('Hello world!')
|
||||
19
test/examples/palette.pk
Normal file
19
test/examples/palette.pk
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## Run pocket palette.pk > palette.ppm
|
||||
## Open palatte.ppm with any image viwer which support ppm image
|
||||
## (ex: photoshop, gimp, libre office draw, ...)
|
||||
|
||||
blue = 200
|
||||
|
||||
print("P3")
|
||||
print(255, 255)
|
||||
print(255)
|
||||
|
||||
from lang import write
|
||||
for r in 0..255
|
||||
for g in 0..255
|
||||
write(r, ' ', g, ' ', blue, ' ')
|
||||
end
|
||||
write('\n')
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
17
test/examples/pi.pk
Normal file
17
test/examples/pi.pk
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## PI approximation using Leibniz formula.
|
||||
##
|
||||
## PI/4 = 1 - 1/3 + 1/5 - 1/7 + 1/9 - ...
|
||||
|
||||
from math import abs
|
||||
|
||||
pi_by_4 = 0; sign = -1
|
||||
for i in 1..10000
|
||||
sign *= -1
|
||||
pi_by_4 += sign * 1/(2*i - 1)
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
PI = 4 * pi_by_4
|
||||
assert(abs(PI - 3.141593) < 0.0002)
|
||||
|
||||
print('PI =', PI)
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## Prime numbers.
|
||||
|
||||
res = ''
|
||||
|
||||
def is_prime(n)
|
||||
if n < 2 then return false end
|
||||
for i in 2..n
|
||||
@ -12,12 +10,16 @@ def is_prime(n)
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
def get_all_primes(n)
|
||||
res = []
|
||||
for i in 0..n
|
||||
if is_prime(i)
|
||||
res += to_string(i) + ' '
|
||||
list_append(res, i)
|
||||
end
|
||||
end
|
||||
return res
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
get_all_primes(20)
|
||||
assert(res == '2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 ')
|
||||
primes = get_all_primes(20)
|
||||
assert(primes == [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19])
|
||||
|
||||
print('primes =', primes)
|
||||
|
||||
50
test/run.py
50
test/run.py
@ -1,7 +1,11 @@
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
import json, os
|
||||
import subprocess, os, sys
|
||||
import json, re
|
||||
from os.path import join
|
||||
|
||||
files = [
|
||||
FMT_PATH = "%-25s"
|
||||
INDENTATION = ' | '
|
||||
|
||||
test_files = [
|
||||
"lang/basics.pk",
|
||||
"lang/functions.pk",
|
||||
"lang/if.pk",
|
||||
@ -9,12 +13,44 @@ files = [
|
||||
"examples/prime.pk",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_PATH = "%-25s"
|
||||
INDENTATION = ' | '
|
||||
benchmarks = {
|
||||
"factors" : ['.pk', '.py', '.rb', '.wren'],
|
||||
"fib" : ['.pk', '.py', '.rb', '.wren'],
|
||||
"list_reverse" : ['.pk', '.py', '.rb'],
|
||||
"loop" : ['.pk', '.py', '.rb', ".wren"],
|
||||
"primes" : ['.pk', '.py', '.rb', ".wren"],
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def run_all_benchmarks():
|
||||
print("--------------------------------")
|
||||
print(" BENCHMARKS ")
|
||||
print("--------------------------------")
|
||||
|
||||
def get_interpreter(file):
|
||||
if file.endswith('.pk' ) : return 'pocket'
|
||||
if file.endswith('.py' ) : return 'python'
|
||||
if file.endswith('.rb' ) : return 'ruby'
|
||||
if file.endswith('.wren') : return 'wren'
|
||||
assert False
|
||||
|
||||
for bm_name in benchmarks:
|
||||
print(bm_name + ":")
|
||||
for ext in benchmarks[bm_name]:
|
||||
file = join('benchmark', bm_name, bm_name + ext)
|
||||
interpreter = get_interpreter(file)
|
||||
print(' %10s: '%interpreter, end=''); sys.stdout.flush()
|
||||
result = run_command([interpreter, file])
|
||||
time = re.findall(r'elapsed:\s*([0-9\.]+)\s*s',
|
||||
result.stdout.decode('utf8'),
|
||||
re.MULTILINE)
|
||||
assert len(time) == 1, r'elapsed:\s*([0-9\.]+)\s*s --> no mach found.'
|
||||
print('%10ss'%time[0])
|
||||
|
||||
def run_all_tests():
|
||||
for path in files:
|
||||
print("--------------------------------")
|
||||
print(" TESTS ")
|
||||
print("--------------------------------")
|
||||
for path in test_files:
|
||||
run_file(path)
|
||||
|
||||
def run_file(path):
|
||||
@ -37,4 +73,4 @@ def run_command(command):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
run_all_tests()
|
||||
|
||||
run_all_benchmarks()
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user