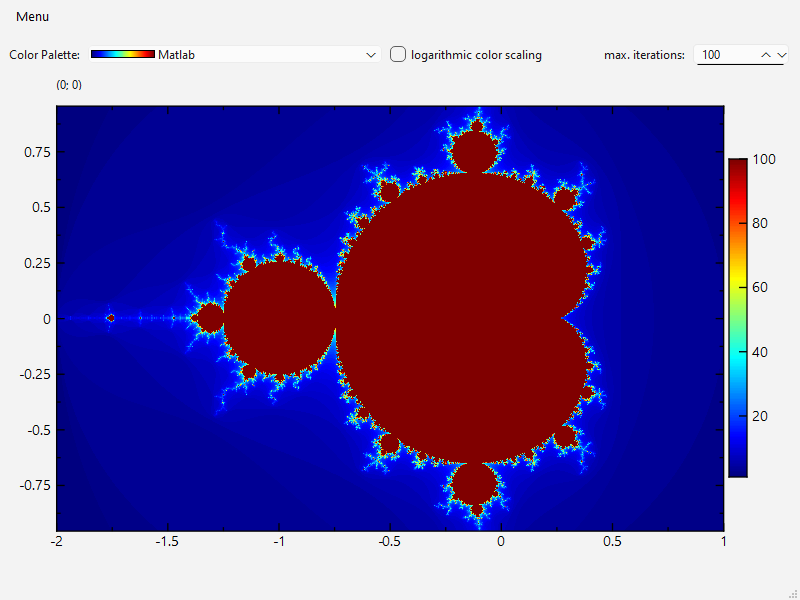
9.1 KiB
Example (JKQTPlotter): Mandelbrot Set Explorer
Introduction and Usage
This project (see ./examples/mandelbrot/) shows how to calculate and visualize the Mandelbrot set using JKQTPlotter and its JKQTPMathImage.
The source code of the main application is (see mandelbrot.cpp:
You can use any of the several zooming methods (by mouse-wheel, panning, by drawing a rectangle ...) and the application will automaticaly calculate the zoomed area. Here is an example:
- Select the Zoom by Mouse Rectangle tool:
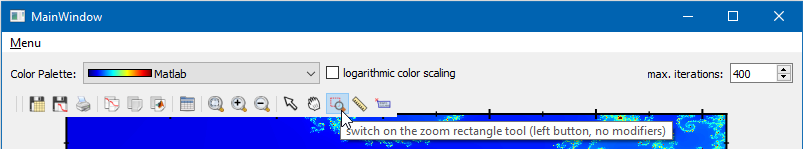
- Drag open a rectangle that you want to zoom into:
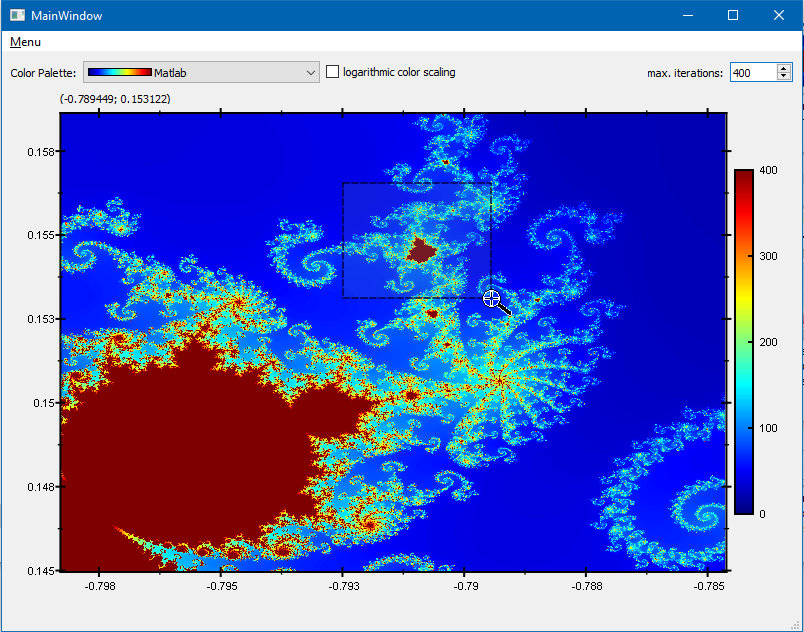
- When you release the mouse, the new image will be calculated.
How it works
In the constructor, the ui, containing a JKQTPlotter ui->plot, is initialized. Then the JKQTPlotter is set up:
// 1. set the graph scales manually
ui->plot->setXY(-2,1,-1,1);
ui->plot->setAbsoluteXY(-5,5,-5,5);
// 2. set the asxpect ratio to width/height
ui->plot->getPlotter()->setMaintainAspectRatio(true);
ui->plot->getPlotter()->setAspectRatio(static_cast<double>(ui->plot->width())/static_cast<double>(ui->plot->height()));
// 3. disable grids
ui->plot->getXAxis()->setDrawGrid(false);
ui->plot->getYAxis()->setDrawGrid(false);
Then a JKQTPMathImage is added which displays an image column mandelbrot_col_display:
graph=new JKQTPColumnMathImage(ui->plot);
graph->setTitle("");
// image column with the data
graph->setImageColumn(mandelbrot_col_display);
// image color range is calculated manually!
graph->setAutoImageRange(false);
graph->setImageMin(0);
graph->setImageMax(ui->spinMaxIterations->value());
// set image size
graph->setX(ui->plot->getXMin());
graph->setY(ui->plot->getYMin());
graph->setWidth(ui->plot->getXMax()-ui->plot->getXMin());
graph->setHeight(ui->plot->getYMax()-ui->plot->getYMin());
// add graph to plot
ui->plot->addGraph(graph);
In between thise two code blocks, two image columns are added to the internal JKQTPDatastore:
mandelbrot_col=ds->addImageColumn(300,200, "mandelbrot_image_calculate");
mandelbrot_col_display=ds->copyColumn(mandelbrot_col, "mandelbrot_image_display");
As mentioned before, mandelbrot_col_display is used for plotting and the baclground column (of the same size) mandelbrot_col is used to calculate a new image:
calculateMandelSet(ui->plot->getXMin(), ui->plot->getXMax(), ui->plot->getYMin(), ui->plot->getYMax(), 300, 200, ui->spinMaxIterations->value());
When calculation finished, the contents of mandelbrot_col is copied to mandelbrot_col_display:
ui->plot->getDatastore()->copyColumnData(mandelbrot_col_display, mandelbrot_col);
In order to implement the zoom functionality, the signal JKQTPlotter::zoomChangedLocally is connected to a function, which recalculates the new image for the new zoom-range:
void MandelbrotMainWindow::plotZoomChangedLocally(double newxmin, double newxmax, double newymin, double newymax, JKQTPlotter */*sender*/)
{
calculateMandelSet(newxmin, newxmax, newymin, newymax, ui->plot->getXAxis()->getParentPlotWidth(), ui->plot->getYAxis()->getParentPlotWidth(), ui->spinMaxIterations->value());
ui->plot->getDatastore()->copyColumnData(mandelbrot_col_display, mandelbrot_col);
if (ui->chkLogScaling->isChecked()) {
std::transform(ui->plot->getDatastore()->begin(mandelbrot_col), ui->plot->getDatastore()->end(mandelbrot_col), ui->plot->getDatastore()->begin(mandelbrot_col), &log10);
}
graph->setX(newxmin);
graph->setY(newymin);
graph->setWidth(newxmax-newxmin);
graph->setHeight(newymax-newymin);
// this call ensures correctly set NX and NY
graph->setImageColumn(mandelbrot_col_display);
ui->plot->redrawPlot();
}
The actual calculation is performed in calculateMandelSet():
void MandelbrotMainWindow::calculateMandelSet(double rmin, double rmax, double imin, double imax, size_t width, size_t height, unsigned int max_iterations) {
QElapsedTimer timer;
timer.start();
auto ds=ui->plot->getDatastore();
// ensure the image column has the correct size
ds->resizeImageColumn(mandelbrot_col, width, height);
qDebug()<<"calculating for "<<width<<"x"<<height<<"pixels: real="<<rmin<<"..."<<rmax<<", imaginary="<<imin<<"..."<<imax;
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// iterate over all pixels, serial code
for (auto pix=ds->begin(mandelbrot_col); pix!= ds->end(mandelbrot_col); ++pix) {
// calculate the pixels coordinate in the imaginary plane
const double r0=static_cast<double>(pix.getImagePositionX())/static_cast<double>(width)*(rmax-rmin)+rmin;
const double i0=static_cast<double>(pix.getImagePositionY())/static_cast<double>(height)*(imax-imin)+imin;
//qDebug()<<pix.getImagePositionX()<<","<<pix.getImagePositionY()<<": "<<r0<<","<<i0;
unsigned int iteration=0;
double ri=0;
double ii=0;
// check for Mandelbrot series divergence at r0, i0, i.e. calculate
// the series [r(i),i(i)]=fmanelbrot(r(i-1),i(i-1) | r0,i0) for every point in the plane [r0,i0]
// starting from r(0)=i(0)=0. The number of iterations until |r(i),i(i)|>=2 gives the color of
// the point.
while(ri*ri+ii*ii<=2.0*2.0 && iteration<max_iterations) {
const double tmp=ri*ri-ii*ii+r0;
ii=2.0*ri*ii+i0;
ri=tmp;
iteration++;
}
*pix=iteration;
}
qDebug()<<"finished calculating after "<<static_cast<double>(timer.nsecsElapsed())/1000000.0<<"ms";
}
Here the actual algorithm to calculate the mandelbrot set is implemented. It iterates over all pixels pix in mandelbrot_col and updates their value according to the result of the calculation with *pix=iteration;.
In order to speed up the program, it actually uses a parallelized version of the algorithm:
void MandelbrotMainWindow::calculateMandelSet(double rmin, double rmax, double imin, double imax, size_t width, size_t height, unsigned int max_iterations) {
QElapsedTimer timer;
timer.start();
auto ds=ui->plot->getDatastore();
// ensure the image column has the correct size
ds->resizeImageColumn(mandelbrot_col, width, height);
qDebug()<<"calculating for "<<width<<"x"<<height<<"pixels: real="<<rmin<<"..."<<rmax<<", imaginary="<<imin<<"..."<<imax;
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// iterate over all pixels, parallelized version
// calculate the block size for parallel processing
const size_t blocksize=std::max<size_t>(100,width*height/std::max<size_t>(2, std::thread::hardware_concurrency()-1));
std::vector<std::thread> threads;
for (size_t offset=0; offset<width*height; offset+=blocksize) {
threads.push_back(std::thread([=](){
// start iterating at begin+offset
auto pix=ds->begin(mandelbrot_col)+static_cast<int>(offset);
// stop iterating at begin+offset+blocksize, or at the end
const auto pix_end=pix+static_cast<int>(blocksize);
for (; pix!=pix_end; ++pix) {
// calculate the pixels coordinate in the imaginary plane
const double r0=static_cast<double>(pix.getImagePositionX())/static_cast<double>(width)*(rmax-rmin)+rmin;
const double i0=static_cast<double>(pix.getImagePositionY())/static_cast<double>(height)*(imax-imin)+imin;
//qDebug()<<pix.getImagePositionX()<<","<<pix.getImagePositionY()<<": "<<r0<<","<<i0;
unsigned int iteration=0;
double ri=0;
double ii=0;
// check for Mandelbrot series divergence at r0, i0, i.e. calculate
// the series [r(i),i(i)]=fmanelbrot(r(i-1),i(i-1) | r0,i0) for every point in the plane [r0,i0]
// starting from r(0)=i(0)=0. The number of iterations until |r(i),i(i)|>=2 gives the color of
// the point.
while(ri*ri+ii*ii<=2.0*2.0 && iteration<max_iterations) {
const double tmp=ri*ri-ii*ii+r0;
ii=2.0*ri*ii+i0;
ri=tmp;
iteration++;
}
*pix=iteration;
}
}));
}
qDebug()<<" using "<<threads.size()<<" threads with blocksize="<<blocksize;
// wait for threads to finish
for (auto& thread:threads) thread.join();
threads.clear();
qDebug()<<"finished calculating after "<<static_cast<double>(timer.nsecsElapsed())/1000000.0<<"ms";
}