| .. | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| imageplot_modifier_and_lib.pro | ||
| imageplot_modifier.cpp | ||
| imageplot_modifier.pro | ||
| README.md | ||
Example (JKQTPlotter): Simple math image plot with modifier datat
This project (see ./examples/imageplot_modifier/) creates a JKQTPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds a color-coded image plot of a mathematical function (here sin(r)). Then a second image (linearly scaling from 1 in the center to 0 at the borders) is used to modify the first image. The modification can alter several properties of the original image, like its saturation, its transparency (alpha) ...
The source code of the main application is (see imageplot_modifier.cpp:
#include <QApplication>
#include <cmath>
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtplotter.h"
#include "jkqtplotter/graphs/jkqtpimage.h"
#ifndef M_PI
#define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846
#endif
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
JKQTPlotter plot;
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore (for convenience)
plot.getPlotter()->setUseAntiAliasingForGraphs(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
plot.getPlotter()->setUseAntiAliasingForSystem(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
plot.getPlotter()->setUseAntiAliasingForText(true); // nicer (but slower) text rendering
JKQTPDatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
// 2. now we create data for the charts (taken from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Energiemix_Deutschland.svg)
const int NX=150; // image dimension in x-direction [pixels]
const int NY=150; // image dimension in x-direction [pixels]
double image[NX*NY]; // row-major image
double modifier[NX*NY]; // row-major modfier image
// 2 calculate image of airy disk in a row-major array
double x, y=-static_cast<double>(NY)/2.0;
for (int iy=0; iy<NY; iy++ ) {
x=-static_cast<double>(NX)/2.0;
for (int ix=0; ix<NX; ix++ ) {
const double r=sqrt(x*x+y*y);
image[iy*NX+ix] = cos(M_PI*r/20.0);
modifier[iy*NX+ix] = 1.0-r/sqrt(NX*NX/4.0+NY*NY/4.0);
x+=1;
}
y+=1;
}
// 3. make data available to JKQTPlotter by adding it to the internal datastore.
// In this step the contents of C-array airydisk is copied into a column
// of the datastore in row-major order
size_t cImage=ds->addCopiedImageAsColumn(image, NX, NY, "imagedata");
size_t cModifier=ds->addCopiedImageAsColumn(modifier, NX, NY, "modifier");
// 4. create a graph (JKQTPColumnMathImage) with the column created above as data
// The data is color-coded with the color-palette JKQTPMathImageMATLAB
// the converted range of data is determined automatically because setAutoImageRange(true)
JKQTPColumnMathImage* graph=new JKQTPColumnMathImage(&plot);
graph->setTitle("");
// image column with the data
graph->setImageColumn(cImage);
// now set the modifier image:
graph->setModifierColumn(cModifier);
graph->setAutoModifierRange(true);
// ... and specify which image property is modified (here the saturation, but ModifyAlpha for the transparency and ModifyValue from the HSV color-model are also possible):
graph->setModifierMode(JKQTPMathImageBase::ModifySaturation);
// set size of the data (the datastore does not contain this info, as it only manages 1D columns of data and this is used to assume a row-major ordering
graph->setNx(NX);
graph->setNy(NY);
// where does the image start in the plot, given in plot-axis-coordinates (bottom-left corner)
graph->setX(-NX/2.0);
graph->setY(-NX/2.0);
// width and height of the image in plot-axis-coordinates
graph->setWidth(NX);
graph->setHeight(NY);
// color-map is "MATLAB"
graph->setColorPalette(JKQTPMathImageMATLAB);
// determine min/max of data automatically and use it to set the range of the color-scale
graph->setAutoImageRange(true);
// 5. add the graphs to the plot, so it is actually displayed
plot.addGraph(graph);
// 6. set axis labels
plot.getXAxis()->setAxisLabel("x [{\\mu}m]");
plot.getYAxis()->setAxisLabel("y [{\\mu}m]");
// 7. fix axis and plot aspect ratio to 1
plot.getPlotter()->setMaintainAspectRatio(true);
plot.getPlotter()->setMaintainAxisAspectRatio(true);
// 8 autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
plot.zoomToFit();
// show plotter and make it a decent size
plot.show();
plot.resize(500,500);
plot.setWindowTitle("JKQTPColumnMathImage");
return app.exec();
}
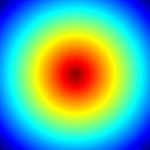
The data image (sin(r/30)) on its own looks like this:

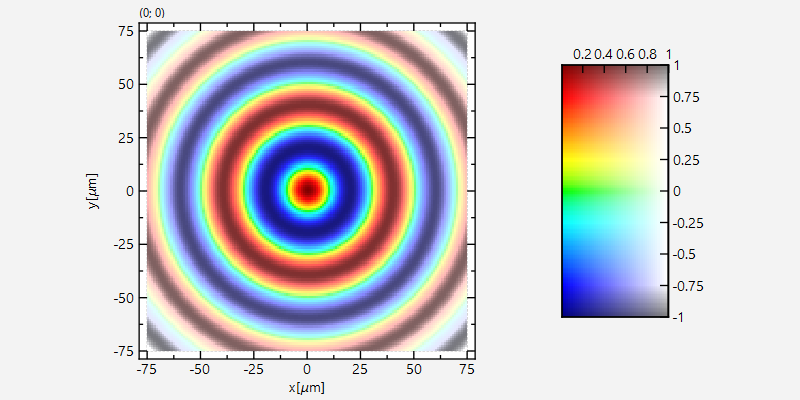
and the modifier image on its own would look like this:
Combined the two form this plot:
There are several modification modes available (see also documentation of JKQTPMathImageBase::ModifierMode):
- no modification
JKQTPMathImageBase::ModifierMode::ModifyNone: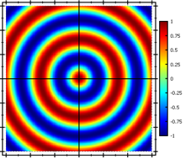
- modify the VALUE-channel from the HSV color space
JKQTPMathImageBase::ModifierMode::ModifyValue: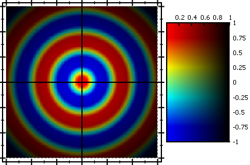
- modify the SATURATION-channel from the HSV color space
JKQTPMathImageBase::ModifierMode::ModifySaturation: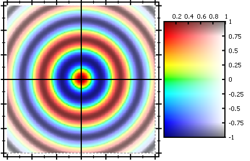
- modify the ALPHA/TRANSPARENCY-channel from the RGBA color space
JKQTPMathImageBase::ModifierMode::ModifyAlpha: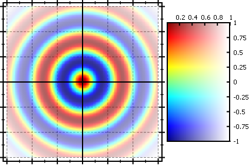
- modify the LUMINANCE-channel from the HSL color space
JKQTPMathImageBase::ModifierMode::ModifyLuminance: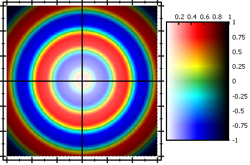
- modify the HUE-channel from the HSV color space
JKQTPMathImageBase::ModifierMode::ModifyHue: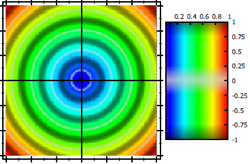
See examples/imageplot for a detailed description of the other possibilities that the class JKQTPColumnMathImage (and also JKQTPMathImage) offer with respect to determining how an image is plotted. You can combine all options there with the modifier feature described here.