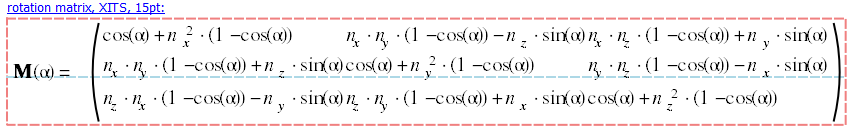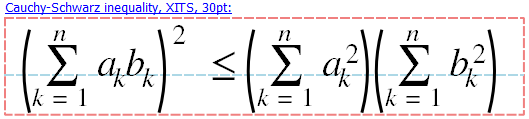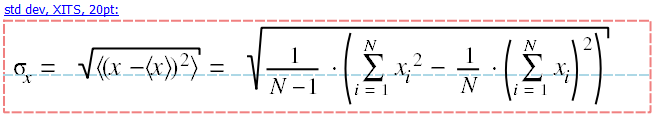| doc | ||
| images | ||
| math_fonts | ||
| screenshots | ||
| test | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| jkqtfastplotter.cpp | ||
| jkqtfastplotter.h | ||
| jkqtmathtext_with_xits.pri | ||
| jkqtmathtext.cpp | ||
| jkqtmathtext.h | ||
| jkqtmathtext.pri | ||
| jkqtmathtext.readme | ||
| jkqtp_imexport.h | ||
| jkqtpbaseelements.cpp | ||
| jkqtpbaseelements.h | ||
| jkqtpbaseplotter.cpp | ||
| jkqtpbaseplotter.h | ||
| jkqtpbaseplotter.qrc | ||
| jkqtpdatastorage.cpp | ||
| jkqtpdatastorage.h | ||
| jkqtpelements.cpp | ||
| jkqtpelements.h | ||
| jkqtpgeoelements.cpp | ||
| jkqtpgeoelements.h | ||
| jkqtphighrestimer.cpp | ||
| jkqtphighrestimer.h | ||
| jkqtpimageelements.cpp | ||
| jkqtpimageelements.h | ||
| jkqtpimagetools.cpp | ||
| jkqtpimagetools.h | ||
| jkqtplotter.cpp | ||
| jkqtplotter.dox | ||
| jkqtplotter.Doxyfile | ||
| jkqtplotter.h | ||
| jkqtplotter.pri | ||
| jkqtplotter.readme | ||
| jkqtpmathparser.cpp | ||
| jkqtpmathparser.h | ||
| jkqtpoverlayelements.cpp | ||
| jkqtpoverlayelements.h | ||
| jkqtpparsedfunctionelements.cpp | ||
| jkqtpparsedfunctionelements.h | ||
| jkqtptools.cpp | ||
| jkqtptools.h | ||
| jkqttools.cpp | ||
| jkqttools.h | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
JKQtPlotter
This is an extensive library of function/data plotter classes for Qt (>= 4.7, tested with Qt up to 5.4).
This software is licensed under the term of the GNU Lesser General Public License 2.1 (LGPL 2.1) or above.
Examples
This section assembles some simple examples of usage. You can find more (complex) examples for the classes in this repository in the subfolder "test". All test-projects are Qt-projects that use qmake to build. You can load them into QtCreator easily.
###Very simple line-graph
This project (see ./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest/) simply creates a JKQtPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds a single line-graph (a sine-wave). Data is initialized from two QVector objects.
The QMake project looks like this (see ./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest/jkqtplotter_simpletest.pro):
# source code for this simple demo
SOURCES = jkqtplotter_simpletest.cpp
# configure Qt
CONFIG += qt
QT += core gui svg
greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets printsupport
# output executable name
TARGET = jkqtplotter_simpletest
# include JKQtPlotter source code
include(../../jkqtplotter.pri)
And the soruce code of the main application is (see ./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest/jkqtplotter_simpletest.cpp):
#include <QApplication>
#include "jkqtplotter.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore
// (for convenience)
JKQtPlotter plot;
JKQTPdatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
// 2. now we create data for a simple plot (a sine curve)
QVector<double> X, Y;
const int Ndata=100;
for (int i=0; i<Ndata; i++) {
const double x=double(i)/double(Ndata)*8.0*M_PI;
X<<x;
Y<<sin(x);
}
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal
// datastore.
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise), so
// you can reuse X and Y afterwards!
// The variables columnX and columnY will contain the internal column ID
// of the newlycreated columns with names "x" and "y" and the (copied)
// data from X and Y.
size_t columnX=ds->addCopiedColumn(X, "x");
size_t columnY=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y, "y");
// 4. create a graph in the plot, which plots the dataset X/Y:
JKQTPxyLineGraph* graph1=new JKQTPxyLineGraph(&plot);
graph1->set_xColumn(columnX);
graph1->set_yColumn(columnY);
graph1->set_title(QObject::tr("sine graph"));
// 5. add the graph to the plot, so it is actually displayed
plot.addGraph(graph1);
// 6. autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
plot.zoomToFit();
// show plotter and make it a decent size
plot.show();
plot.resize(600,400);
return app.exec();
}
###Simple line-graph with error bars
This project (see ./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_symbols_and_errors/) simply creates a JKQtPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds a single line-graph (a sine-wave) that has y-errorbars. In addition, this example shows how to change some of the axis properties and how to use LaTeX markup to format axis labels (can actually be used for all labels in JKQtPlotter). Also, in comparison to the last example, here we initialize the data from C-type arrays (double*), instead of QVector objects.
The soruce code of the main application is (see ./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_symbols_and_errors/jkqtplotter_simpletest_symbols_and_errors.cpp):
#include <QApplication>
#include "jkqtplotter.h"
// number of datapoints:
#define Ndata 10
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore (for convenience)
JKQtPlotter plot;
JKQTPdatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
// 2. now we create data for a simple plot (a sine curve with lin. increasing errors)
double X[Ndata], Y[Ndata], YERROR[Ndata];
for (int i=0; i<Ndata; i++) {
X[i]=double(i)/double(Ndata)*2.0*M_PI;
Y[i]=sin(X[i]);
YERROR[i]=0.2+double(i)/double(Ndata)*0.25;
}
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal datastore.
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise), so you can
// reuse X and Y afterwards!
// the variables columnX and columnY will contain the internal column ID of the newly
// created columns with names "x" and "y" and the (copied) data from X and Y.
size_t columnX=ds->addCopiedColumn(X, Ndata, "x");
size_t columnY=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y, Ndata, "y");
size_t columnYE=ds->addCopiedColumn(YERROR, Ndata, "y-error");
// 4. create a graph in the plot, which plots the dataset X/Y:
JKQTPxyLineErrorGraph* graph1=new JKQTPxyLineErrorGraph(&plot);
graph1->set_xColumn(columnX);
graph1->set_yColumn(columnY);
graph1->set_yErrorColumn(columnYE);
graph1->set_symbol(JKQTPfilledStar); // set symbol style
graph1->set_yErrorStyle(JKQTPerrorBars); // set error indicator type
graph1->set_drawLine(false); // don't draw a line
graph1->set_title(QObject::tr("sine graph"));
// 5. add the graph to the plot, so it is actually displayed
plot.addGraph(graph1);
// 6. hide 0-lines
plot.getXAxis()->set_showZeroAxis(false);
plot.getYAxis()->set_showZeroAxis(false);
// 7. set some axis properties (we use LaTeX for nice equation rendering)
plot.getXAxis()->set_axisLabel(QObject::tr("x-axis $x$ [mm]"));
plot.getYAxis()->set_axisLabel(QObject::tr("\\textbf{\\color{red}{y-axis} $\\left(y=\\sin(x)\\pm(0.2+0.25\\cdot x)\\right)$ [A.U.]}"));
plot.getXAxis()->set_labelFont("Arial");
plot.getYAxis()->set_labelFont("Times New Roman");
plot.getYAxis()->set_labelFontSize(12); // large x-axis label
plot.getYAxis()->set_tickLabelFontSize(10); // and larger y-axis tick labels
// 8. autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
plot.zoomToFit();
// show plotter and make it a decent size
plot.show();
plot.resize(600,400);
return app.exec();
}
###Simple barchart
This project (see ./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_barchart/) simply creates a JKQtPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds a single line-graph (a sine-wave) that has y-errorbars. In addition, this example shows how to change some of the axis properties and how to use LaTeX markup to format axis labels (can actually be used for all labels in JKQtPlotter). Also, in comparison to the last example, here we initialize the data from C-type arrays (double*), instead of QVector objects.
The soruce code of the main application is (see ./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_barchart/jkqtplotter_simpletest_barchart.cpp):
#include <QApplication>
#include "jkqtplotter.h"
#define Ndata 5
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore (for convenience)
JKQtPlotter plot;
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForGraphs(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForSystem(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForText(true); // nicer (but slower) text rendering
JKQTPdatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
// 2. now we create data for three simple barchart
QString L[Ndata]={ "cat. A", "cat. B", "cat. C", "cat. D", "other"};
double X[Ndata]={ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
double Y1[Ndata]={ 5, 4, 3, 4, 5};
double Y2[Ndata]={ -5, -3, 1, 3, 6};
double Y3[Ndata]={ 6, 2, 5, 3, 6};
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal datastore.
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise)
// the variables columnX and columnY... will contain the internal column ID of the
// newly created columns with names "x" and "y..." and the (copied) data from X
// and Y...
size_t columnX=ds->addCopiedColumn(X, Ndata, "x");
size_t columnY1=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y1, Ndata, "y1");
size_t columnY2=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y2, Ndata, "y2");
size_t columnY3=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y3, Ndata, "y3");
// 4. create graphs in the plot, which plots the dataset X/Y1, X/Y2 and X/Y3:
JKQTPbarHorizontalGraph* graph1=new JKQTPbarHorizontalGraph(&plot);
graph1->set_xColumn(columnX);
graph1->set_yColumn(columnY1);
graph1->set_title(QObject::tr("dataset 1"));
JKQTPbarHorizontalGraph* graph2=new JKQTPbarHorizontalGraph(&plot);
graph2->set_xColumn(columnX);
graph2->set_yColumn(columnY2);
graph2->set_title(QObject::tr("dataset 2"));
JKQTPbarHorizontalGraph* graph3=new JKQTPbarHorizontalGraph(&plot);
graph3->set_xColumn(columnX);
graph3->set_yColumn(columnY3);
graph3->set_title(QObject::tr("dataset 3"));
// 5. add the graphs to the plot, so it is actually displayed
plot.addGraph(graph1);
plot.addGraph(graph2);
plot.addGraph(graph3);
// 6. now we set the graphs, so they are plotted side-by-side
// This function searches all JKQTPbarHorizontalGraph in the current
// plot and sets their shift/scale so they form a nice plot with
// side-by-side groups
graph1->autoscaleBarWidthAndShift(0.75, 1);
// 7. data is grouped into 5 numbere groups (1..5), but we also have string
// labels for these groups (stored in L). In order to display these labels,
// we have to tell the x-Axis to use these special labels:
plot.getXAxis()->addAxisTickLabels(X, L, Ndata);
// also we can rotate the labels a bit (by 45 degree), so they fit better
plot.getXAxis()->set_tickLabelAngle(45);
plot.getXAxis()->set_tickLabelFontSize(12);
// 8. finally we move the plot key/legend to the outside, top-right
// and lay it out as a single row
// NOTE: plot is a descendent of QWidget, which uses an internal object of
// type JKQTBasePlotter, which does the actual plotting.
// So many properties of the plot are only available in this internal
// object, which you can access by plot.get_plotter().
plot.get_plotter()->set_keyPosition(JKQTPkeyOutsideTopRight);
plot.get_plotter()->set_keyLayout(JKQTPkeyLayoutOneRow);
// 9 autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
plot.zoomToFit();
// show plotter and make it a decent size
plot.show();
plot.resize(600,400);
return app.exec();
}
##Screenshots
###Scatter Plots and Boxplots

###Different Types of Barcharts

###Image Plots
You can plot C-arrays as images in different color-coding styles. Diferent Overlays/masks are also available. Finally you can use LaTeX markup to format any axis/plot/tick/... label. there is an internal LaTeX parser in this package.

###Plotting a user-defined (parsed) function
Yes, a complete math expression parser is contained!

###Axis-Label styles in LogLog-Plot

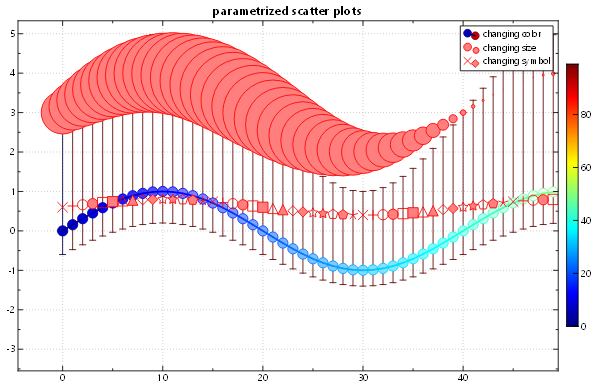
###Parametrized Scatter Plots and Data Viewer
Scatter Plots can have symbols where the shape/color/size is parametrized by a data column. Also the plotter is built around an internal datastore, which you can access (readonly!!!) by a data-viewer that is accessible from the contextmenu in any plot.
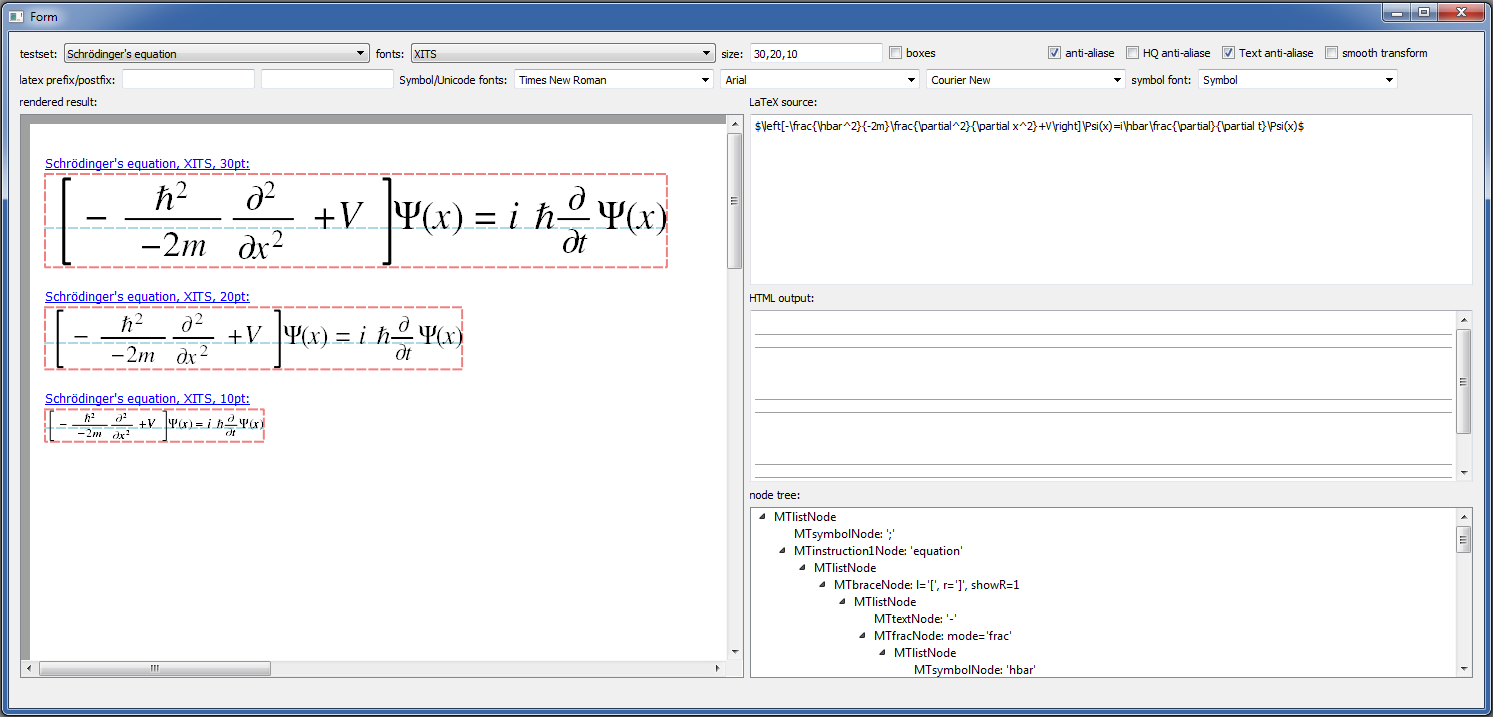
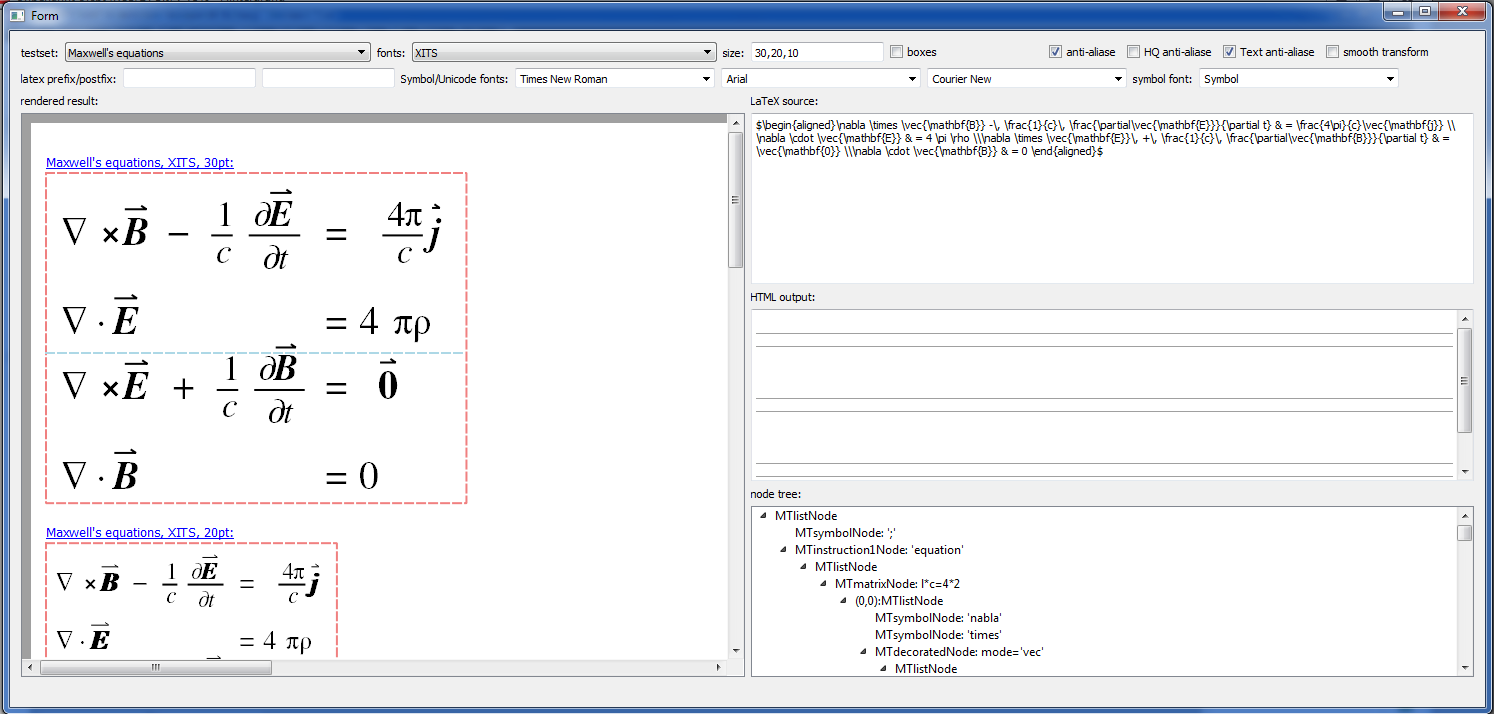
#JKQTmathText
JKQTmathText is a hand-written LaTeX-renderer for Qt (implemented in native C++, using Qt). It supports a large set of standard LaTeX markup and can render it to a QPainter.