| .. | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| multithreaded_thread.h | ||
| multithreaded.cpp | ||
| README.md | ||
Example (JKQTPlotter): Multi-Threaded (Parallel) Plotting
This project (see ./examples/multithreaded/) shows how to use JKQTBasePlotter in multiple threads in parallel.
The source code of the main application can be found in multithreaded.cpp and multithreaded_thread.cpp.
The file multithreaded_thread.cpp contains a QThread class that implements the actual plotting within a static method that is also run inside the thread's QThread::run() method. It generates a plot with several line-graphs and then saves them into a PNG-file:
public:
inline static QString plotAndSave(const QString& filenamepart, int plotIndex, int NUM_GRAPHS, int NUM_DATAPOINTS, double* runtimeNanoseconds=nullptr) {
QElapsedTimer timer;
timer.start();
const QString filename=QDir(QDir::tempPath()).absoluteFilePath(QString("testimg_%1_%2.png").arg(filenamepart).arg(plotIndex));
JKQTBasePlotter plot(true);
const size_t colX=plot.getDatastore()->addLinearColumn(NUM_DATAPOINTS, 0, 10, "x");
QRandomGenerator rng;
for (int i=0; i<NUM_GRAPHS; i++) {
JKQTPXYLineGraph* g;
plot.addGraph(g=new JKQTPXYLineGraph(&plot));
g->setXColumn(colX);
g->setYColumn(plot.getDatastore()->addColumnCalculatedFromColumn(colX, [&](double x) { return cos(x+double(i)/8.0*JKQTPSTATISTICS_PI)+rng.generateDouble()*0.2-0.1;}));
g->setTitle(QString("Plot %1: $f(x)=\\cos\\leftx+\\frac{%1\\pi}{8}\\right)").arg(i+1));
g->setDrawLine(true);
g->setSymbolType(JKQTPNoSymbol);
}
plot.setPlotLabel(QString("Test Plot %1").arg(plotIndex+1));
plot.getXAxis()->setAxisLabel("x-axis");
plot.getYAxis()->setAxisLabel("y-axis");
plot.zoomToFit();
plot.saveAsPixelImage(filename, false, "PNG");
if (runtimeNanoseconds) *runtimeNanoseconds=timer.nsecsElapsed();
return filename;
}
// ...
protected:
inline virtual void run() {
m_filename=plotAndSave(m_filenamepart, m_plotindex, m_NUM_GRAPHS, m_NUM_DATAPOINTS, &m_runtimeNanoseconds);
}
The main application in multithreaded.cpp then uses this method/thread-class to perform a test: First the function is run several times serially and then an equal amount of times in parallel.
#define NUM_PLOTS 8
#define NUM_GRAPHS 6
#define NUM_DATAPOINTS 1000
QElapsedTimer timer;
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// serial plotting
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
timer.start();
for (int i=0; i<NUM_PLOTS; i++) {
PlottingThread::plotAndSave("serial", i, NUM_GRAPHS, NUM_DATAPOINTS);
}
const double durSerialNano=timer.nsecsElapsed();
qDebug()<<"durSerial = "<<durSerialNano/1e6<<"ms";
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// parallel plotting
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
QList<QSharedPointer<PlottingThread>> threads;
for (int i=0; i<NUM_PLOTS; i++) {
qDebug()<<" creating thread "<<i;
threads.append(QSharedPointer<PlottingThread>::create("parallel",i, NUM_GRAPHS, NUM_DATAPOINTS, nullptr));
}
timer.start();
for (int i=0; i<NUM_PLOTS; i++) {
qDebug()<<" staring thread "<<i;
threads[i]->start();
}
for (int i=0; i<NUM_PLOTS; i++) {
qDebug()<<" waiting for thread "<<i;
threads[i]->wait();
}
const double durParallelNano=timer.nsecsElapsed();
qDebug()<<"durParallel = "<<durParallelNano/1e6<<"ms";
threads.clear();
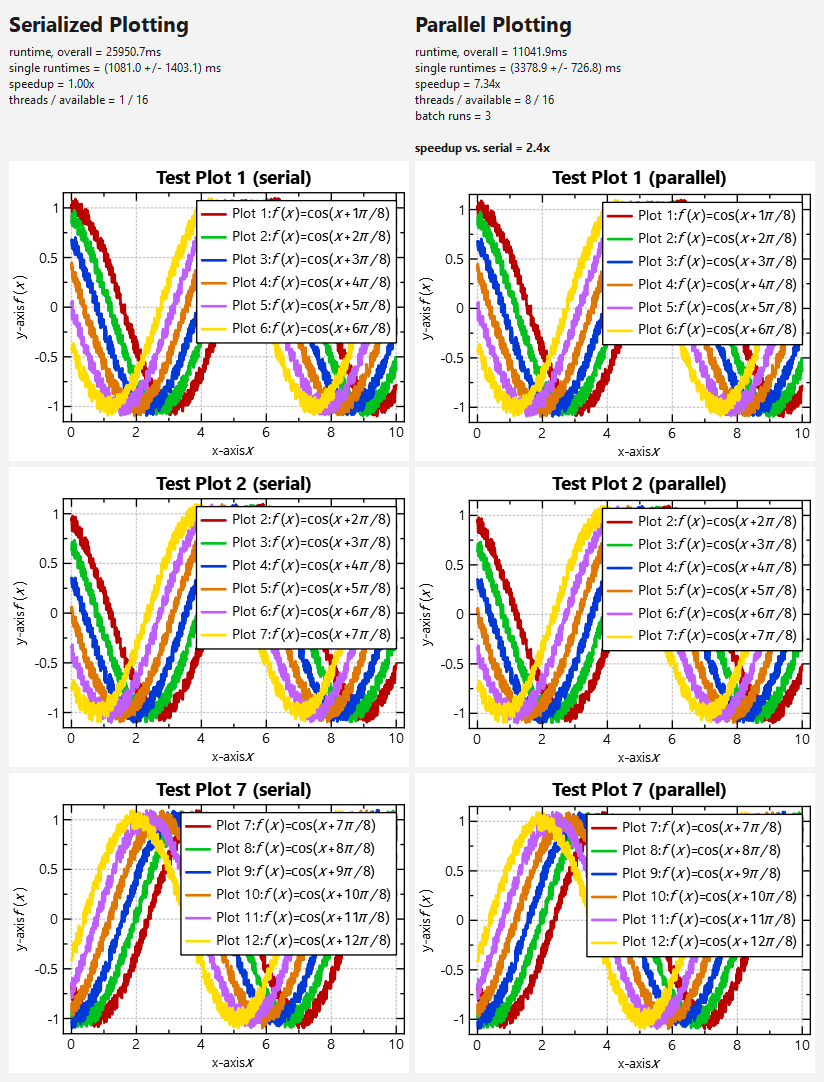
This test results in the following numbers (on my AMD Ryzen5 8/16-core laptop):
VERSION: 5.0.0 BUILD MODE: Release
SERIAL RESULTS:
runtime, overall = 1896.0ms
single runtimes = (236.9 +/- 379.1) ms
speedup = 1.00x
threads / available = 1 / 16
PARALLEL RESULTS:
runtime, overall = 624.7ms
single runtimes = (564.3 +/- 107.7) ms
speedup = 7.23x
threads / available = 8 / 16
speedup vs. serial = 3.0x
From this data you can observe:
- The plotting parallelizes nicely, i.e. the speedup ist >7x on a 8-core-machine. This is the speedup calculated as sum of runtimes of each thread, divided by the runtime of all threads in parallel.
- BUT: the speedup of serialized plotting vs. parallel plotting is way smaller: It is only 2-3x. Also the runtime in each thread is about 3x longer than in the serialized example. This can be explained by the (significant) overhead due to shared caches (and therefore synchronization) between the plotters. This may be reworked in future!
- The variance in runtimes in the (initial) serial test-run is larger than in the parallel run. This is due to filling of the internal caches during the first plotting! .
Finally the application displays the plots: