| .. | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| dateaxes_and_lib.pro | ||
| dateaxes.cpp | ||
| dateaxes.pro | ||
| dateaxes.qrc | ||
| README.md | ||
| weatherdata_gelsenkirchen.csv | ||
| weatherdata_heidelberg_2018-10-14.csv | ||
| weatherdata_heidelberg.csv | ||
Example (JKQTPlotter): Date/Time Axes
[TOC]
Date Axis
This project (see ./examples/dateaxes/) simply creates a JKQTPlotter widget (as a new window) with the X-axis showing time or date(-time) values, formated as such.
The source code of the main application can be found in dateaxes.cpp.
First some data is parsed from a CSV-file (added as ressource to the example). Note that the Time/date or Date+Time data is internally stored as milliseconds since epoc (Jan 1st 1970, 00:00:00), therefore data has to be converted accordingly before beeing added to the graph.
QVector<double> date;
QVector<double> temperature, temperature_min, temperature_max;
// parse a textfile with comments on the first line and the
// semicolon separated data. The first column is a date and time
// the second to fourth columns contain a floating-point number
// with temperature average, min and max
QFile file(":/weatherdata_gelsenkirchen.csv");
file.open(QFile::ReadOnly|QFile::Text);
file.readLine(); // eat comment
while (!file.atEnd()) {
QString line=file.readLine();
QTextStream in(&line);
QStringList items=line.split(";");
// date/time values are stored as doubles representing the corresponding number of milliseconds sind epoch
date<<QDateTime::fromString(items[0], Qt::ISODate).toUTC().toMSecsSinceEpoch();
// store Heidelbergs daily temperature
temperature<<items[1].toDouble();
temperature_min<<items[2].toDouble();
temperature_max<<items[3].toDouble();
}
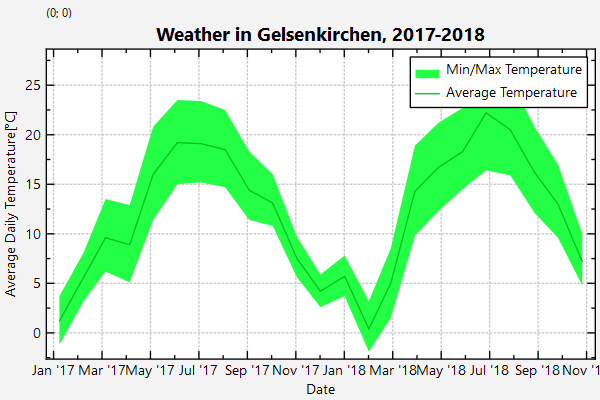
The parsed data looks like this (data was taken from http://wetter.mpg-ge.de/NOAA/NOAA-2018.txt and http://wetter.mpg-ge.de/NOAA/NOAA-2017.txt):
ISO-Date+Time;Temp_mean[degC];Temp_min[degC];Temp_max[degC]
2017-01-15T12:00; 1.2; -1.2; 3.7
2017-02-15T12:00; 5.6; 3.2; 8.1
2017-03-15T12:00; 9.6; 6.2; 13.5
...
Then two graphs are added. One of type JKQTPFilledVerticalRangeGraph plots the range of min+max temperature for each month:
// 3. add a plot for the data mean line (graphTemperature) and range (graphTemperatureRange)
JKQTPFilledVerticalRangeGraph* graphTemperatureRange=new JKQTPFilledVerticalRangeGraph(&plot);
// 4. copy data into datastore and immediately set the yColumn
size_t colDate=ds->addCopiedColumn(date, "date");
graphTemperatureRange->setXColumn(colDate);
graphTemperatureRange->setYColumn(ds->addCopiedColumn(temperature_min, "temperature_min"));
graphTemperatureRange->setYColumn2(ds->addCopiedColumn(temperature_max, "temperature_max"));
// 5. min/max range data
// graph fill color is a lighter shade of the average graph
graphTemperatureRange->setFillColor(graphTemperature->getColor().lighter());
// don't draw lines of the data
graphTemperatureRange->setDrawLine(false);
// plot label in key
graphTemperatureRange->setTitle("Min/Max Temperature");
// add the graph to the plot, so it is actually displayed
plot.addGraph(graphTemperatureRange);
On top of that plot, a second plot is added, which draws the average temperatures of each month as a line:
// 3. add a plot for the data mean line (graphTemperature) and range (graphTemperatureRange)
JKQTPXYLineErrorGraph* graphTemperature=new JKQTPXYLineErrorGraph(&plot);
// 4. copy data into datastore and immediately set the yColumn
size_t colDate=ds->addCopiedColumn(date, "date");
graphTemperature->setXColumn(colDate);
graphTemperature->setYColumn(ds->addCopiedColumn(temperature, "temperature"));
// 5. min/max range data
// .... see above
// 6. average data
// don't use symbols
graphTemperature->setSymbolType(JKQTPNoSymbol);
// set the line width
graphTemperature->setLineWidth(1);
// draw small symbols
graphTemperature->setSymbolSize(6);
// graph title
graphTemperature->setTitle("Average Temperature");
// add the graph to the plot, so it is actually displayed
plot.addGraph(graphTemperature);
Finally the x-axis is formatted to display dates (see [Qt-Documentation of QDateTime::toString()]((http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qdatetime.html#toString) for details on the formating strings):
// 7. format the plot
// set the title above the plot, use LaTeX instructions to make text bold
plot.getPlotter()->setPlotLabel("\\textbf{Weather in Gelsenkirchen, 2017-2018}");
// set x-axis date-time-axis
plot.getXAxis()->setLabelType(JKQTPCALTdatetime);
plot.getXAxis()->setAxisLabel("Date");
// set format string for date axis (e.g. Jan '18), see Documentation of QDateTime::toString()
plot.getXAxis()->setTickDateTimeFormat("MMM ''yy");
// set y-axis temperature axis
plot.getYAxis()->setAxisLabel("Average Daily Temperature [{\\degree}C]");
The result looks like this:
Time Axis
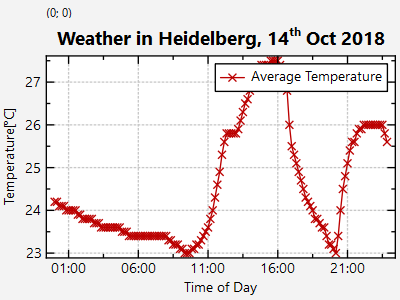
A second variant (see the example CPP-file) displays data with a time-axis:
For that example data-pasring is a bit different, because the file only contains times and no dates:
// 2. now we create data vectors with data parsed from a CSV-file
QVector<double> time;
QVector<double> temperature;
// parse a textfile with comments on the first line and the
// semicolon separated data. The first column is a time
// the second contain a floating-point number with temperatures
QFile file(":/weatherdata_heidelberg_2018-10-14.csv");
file.open(QFile::ReadOnly|QFile::Text);
file.readLine(); // eat comment
while (!file.atEnd()) {
QString line=file.readLine();
QTextStream in(&line);
QStringList items=line.split(";");
// date/time values are stored as doubles representing the corresponding
// number of milliseconds sind epoch. Since the data is time only, we have to use an arbitrary
// date as basis
time<<QDateTime::fromString("1970-01-01T"+items[0], Qt::ISODate).toUTC().toMSecsSinceEpoch();
// store Heidelbergs daily temperature
temperature<<items[1].toDouble();
}
The parsed data looks like this:
Time; Temperature [degC]
00:00:00; 24.2
00:10:00; 24.2
00:20:00; 24.1
00:30:00; 24.1
...
Axis formating for this example is done like this:
// 7. format the plot
// set the title above the plot, use LaTeX instructions to make text bold
plot.getPlotter()->setPlotLabel("\\textbf{Weather in Heidelberg, 14^{th} Oct 2018}");
// set x-axis date-time-axis
plot.getXAxis()->setLabelType(JKQTPCALTtime);
plot.getXAxis()->setAxisLabel("Time of Day");
// set format string for time axis with 24-hour and minute only,
// see QDateTime::toString() documentation for details on format strings
plot.getXAxis()->setTickTimeFormat("HH:mm");
// set y-axis temperature axis
plot.getYAxis()->setAxisLabel("Temperature [{\\degree}C]");