mirror of
https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter.git
synced 2025-01-27 16:09:15 +08:00
| .. | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| example.bmp | ||
| README.md | ||
| rgbimageplot_qt_and_lib.pro | ||
| rgbimageplot_qt.cpp | ||
| rgbimageplot_qt.pro | ||
| rgbimageplot_qt.qrc | ||
Example (JKQTPlotter): QImage as a Graph
This project (see ./examples/rgbimageplot_qt/) simply creates a JKQTPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds an image plot with an image taken from a QImage object.
The source code of the main application is (see rgbimageplot_qt.cpp. the main parts are:
// 2. now we open a BMP-file and load it into an OpenCV cv::Mat
QImage image(":/example.bmp");
// 3. create a graph (JKQTPImage) with a pointer to the QImage-object, generated above
JKQTPImage* graph=new JKQTPImage(&plot);
graph->setTitle("");
// copy the image into the graph (optionally you could also give a pointer to a QImage,
// but then you need to ensure that the QImage is available as long as the JKQTPImage
// instace lives)
graph->setImage(image);
// where does the image start in the plot, given in plot-axis-coordinates (bottom-left corner)
graph->setX(0);
graph->setY(0);
// width/height of the image in plot coordinates
graph->setWidth(image.width());
graph->setHeight(image.height());
// 4. add the graphs to the plot, so it is actually displayed
plot.addGraph(graph);
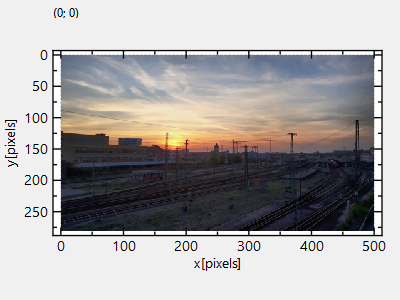
The result looks like this:
The image is upside-down, because computer images use a coordinate system with 0 at the top-left (left-handed coordinate system) and the JKQTPlotter has its 0 at the bottom-left (right-handed coordinate system).
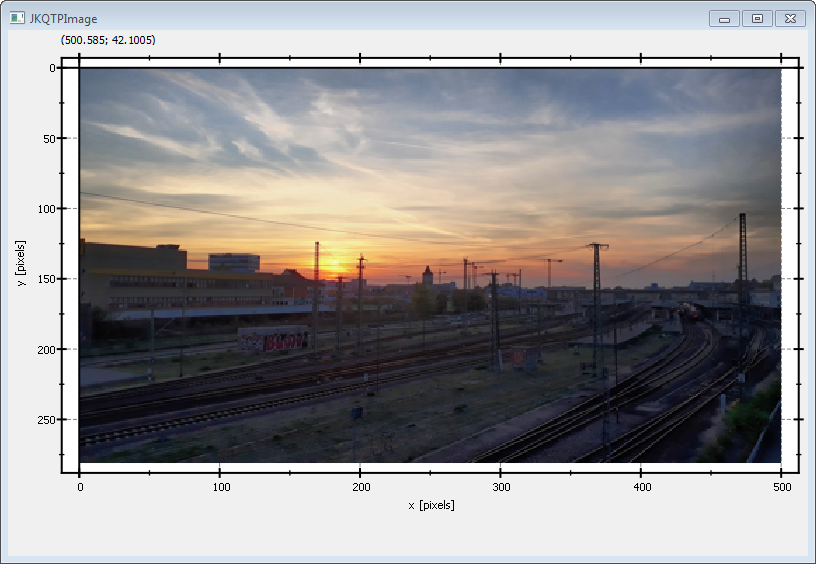
You can modify the program above to display the image in the correct orientation, by adding the line
// 6.1 invert y-axis, so image is oriented correctly
plot.getYAxis()->setInverted(true);
This will reorient the y-axis to point from top to bottom (for increasing positive coordinates):