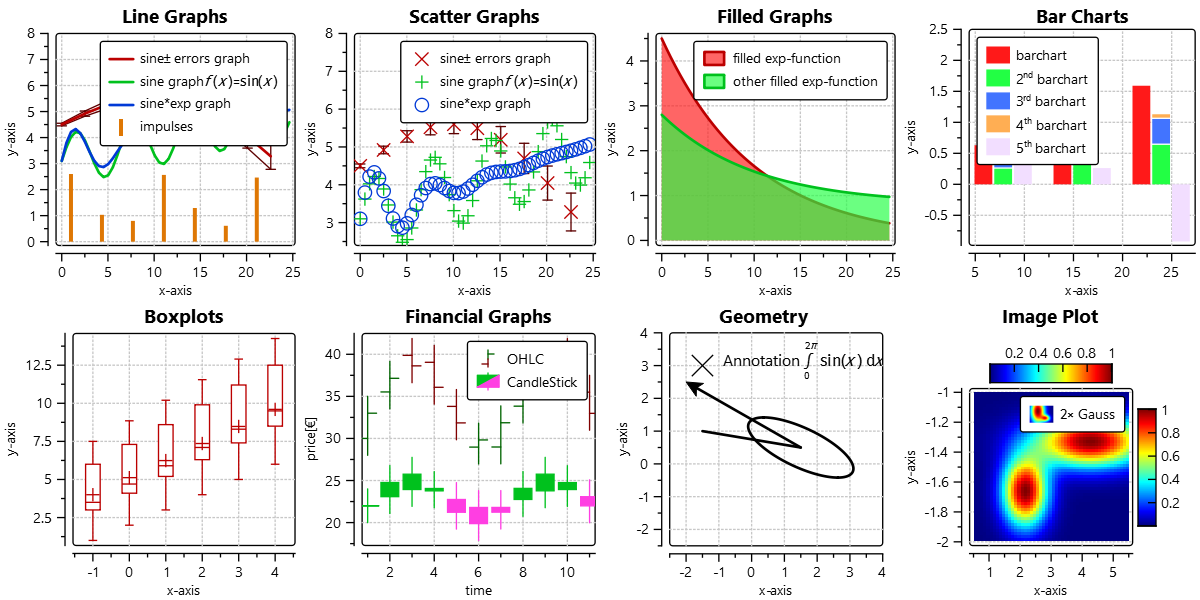
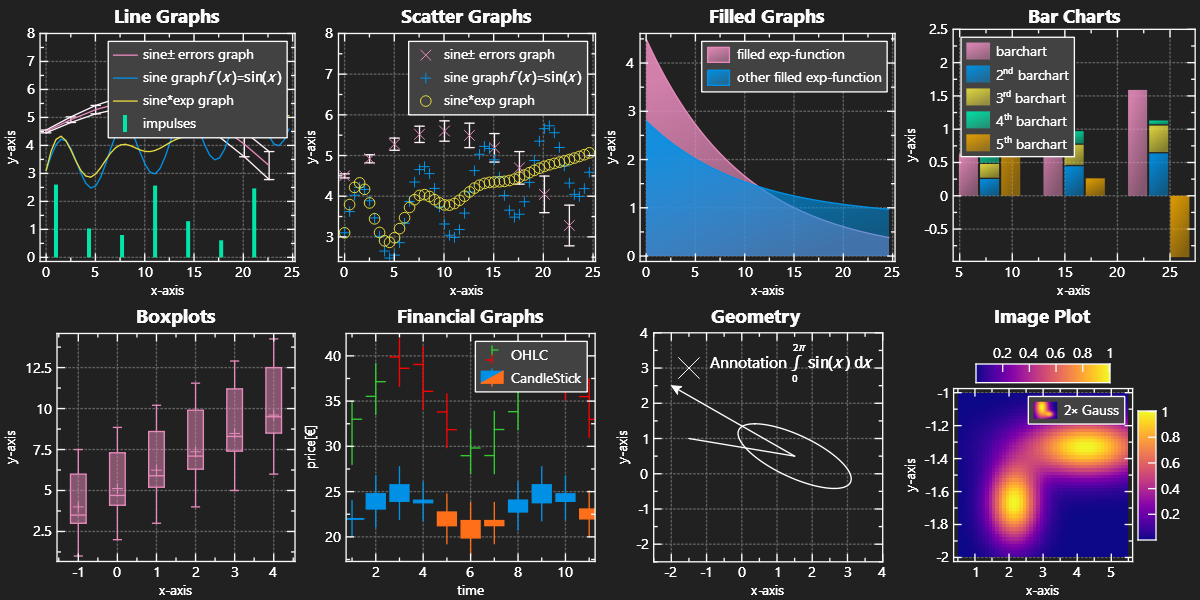
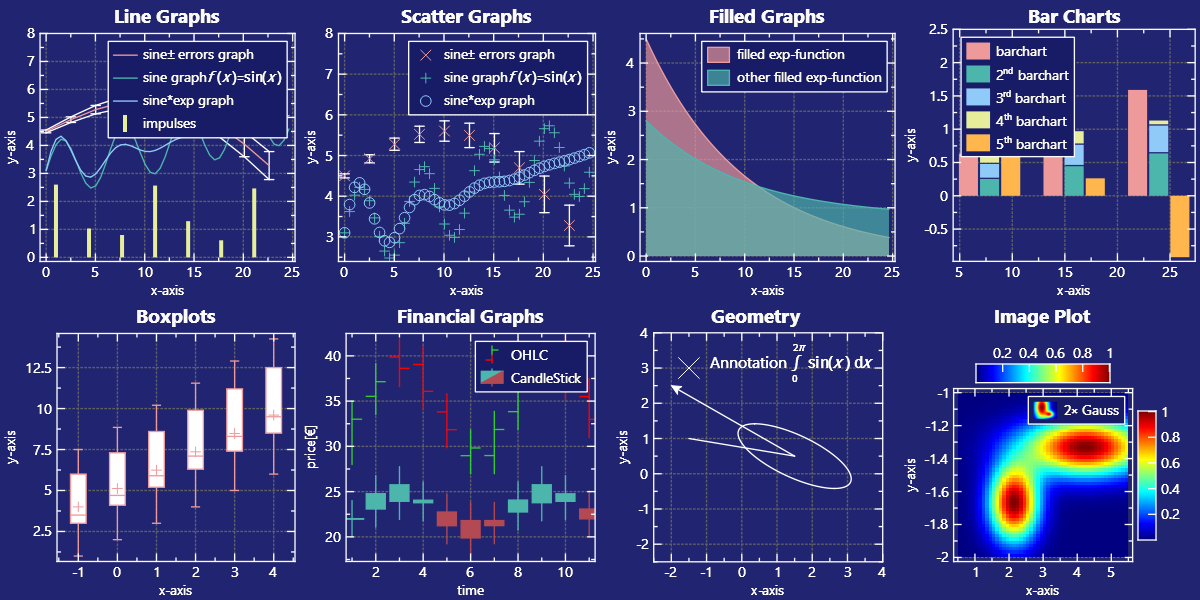
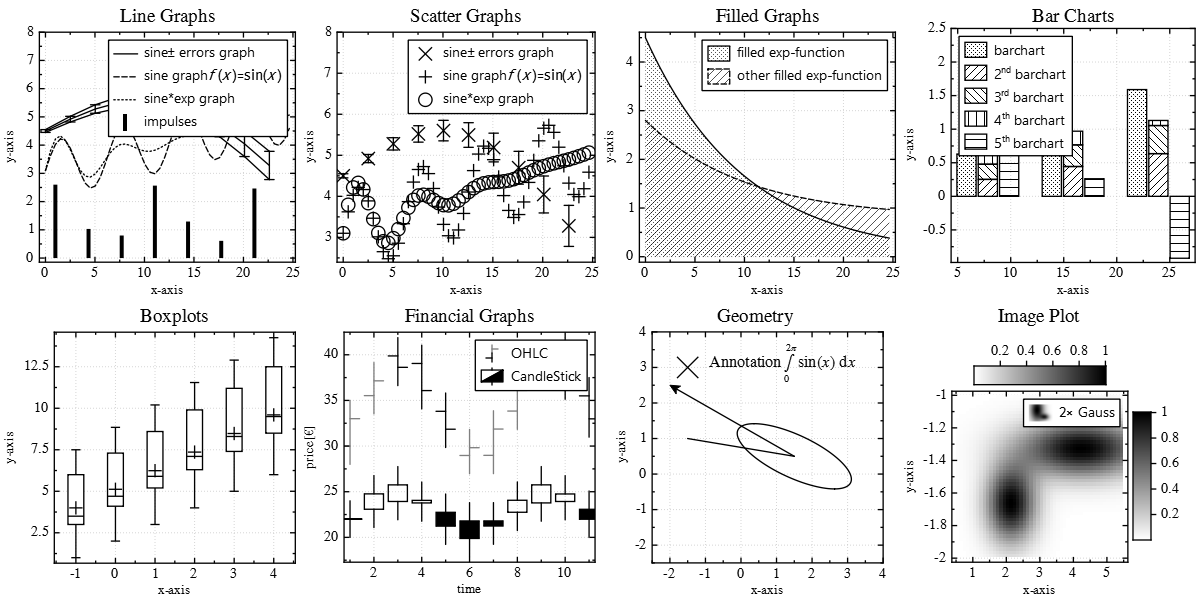
IMPROVED/REWORKED: legend/key positioning as combination of 3 values, e.g. \c JKQTPKeyOutsideTop|JKQTPKeyTop|JKQTPKeyRight or \c JKQTPKeyInside|JKQTPKeyTopJKQTPKeyRight |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| build_test_graphs.h | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| jkqtpstyleplaintextedit.cpp | ||
| jkqtpstyleplaintextedit.h | ||
| README.md | ||
| test_styling_and_lib.pro | ||
| test_styling_main.cpp | ||
| test_styling.cpp | ||
| test_styling.h | ||
| test_styling.pro | ||
| test_styling.ui | ||
Tutorial (JKQTPlotter): Styling a JKQtPlotter
[TOC]
Basic Description
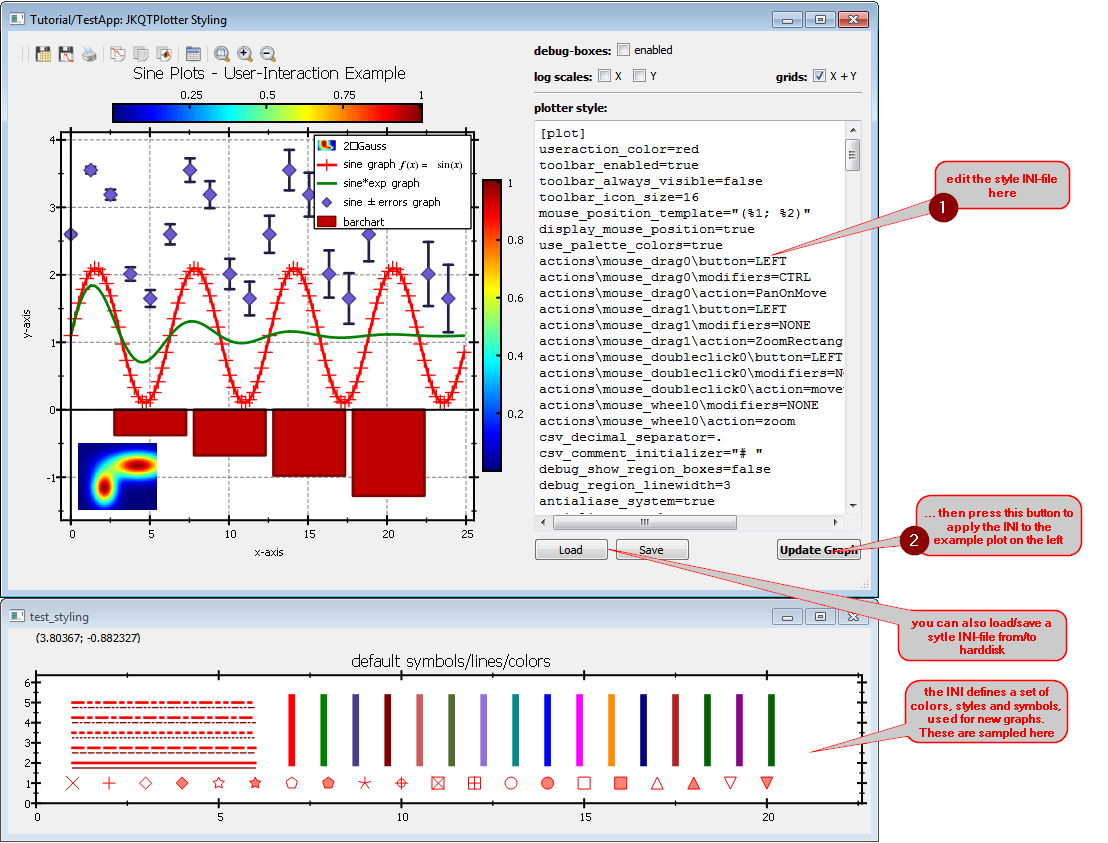
This project (see ./examples/test_styling/) demonstrates different types of user-interactions in JKQTPlotter.
It contains a simple plot with two graphs and provides several widgets that allow to modify the plot styling by editing an INI file:
Altering the Default Style
Global/System-wide Settings
The main()-function can be found in test_styling_main.cpp. Here the Qt application is initialized in the usual way and the main window win is created and shown. After instanciating the QApplication, but befor instanciating the window (and thus the JKQTPlotter), you can already alter the system-wide default styling. It is accessible via the function JKQTPGetSystemDefaultStyle(), which returns a reference to the central style object of type JKQTPlotterStyle. In the example below, the color of the user-actions (e.g. of the zooming rectangle, that can be drawn with the mouse) is set to red:
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
// you can set the system-wide default style properties early on
// all JKQTPlotter instance created after this, will use these
// settings as their initial settings
JKQTPGetSystemDefaultStyle().userActionFontSize=10;
TestStyling win;
win.show();
return app.exec();
}
In addition to JKQTPGetSystemDefaultStyle(), which allows to style the JKQTPlotter (mainly the GUI-parts and user-action bindings), there is also JKQTPGetSystemDefaultBaseStyle(), which accesses a central instance of JKQTBasePlotterStyle. The latter object contains the styling of the graph itself (colors, axis properties, ...).
You can also store these settings in an INI-file (or any file supported by QSettings) and load such a file on startup, using:
QSettings plotSettings("JKQTPlotterSettings.ini", QSettings::IniFormat);;
JKQTPGetSystemDefaultStyle().loadSettings(plotSettings);
JKQTPGetSystemDefaultBaseStyle().loadSettings(plotSettings);
Apply a new Style to an Existing JKQTPlotter
The major part of the source code of the main application can be found in test_styling.cpp. It opens a window with a plotter, that contains a set of test graphs to demonstrate the styling. The following function is connected to the "Update Graph"-button and applys the style defined by the INI in the plainTextEdit to the plotter:
void TestStyling::on_btnUpdate_clicked()
{
QApplication::setOverrideCursor(QCursor(Qt::WaitCursor));
// In this function, we store the data from the plainTextEdit into a temporary file
// tmpfn and the use that file's contents to create a QSettings object, which is used
// to read the plotterStyle into the JKQTPlotter-object ui->plot (using loadCurrentPlotterStyle(settings) )
QString tmpfn=QDir::tempPath()+"/jkqtplotter_config.tmp";
{
QFile data(tmpfn);
if (data.open(QFile::WriteOnly|QFile::Text)) {
QTextStream out(&data);
out << ui->plainTextEdit->toPlainText();
}
}
{
QSettings settings(tmpfn, QSettings::IniFormat);
ui->plot->loadCurrentPlotterStyle(settings);
initPlot();
ui->chkDebugBoxes->setChecked(ui->plot->getPlotter()->isDebugShowRegionBoxesEnabled());
}
QFile::remove(tmpfn);
QApplication::restoreOverrideCursor();
}
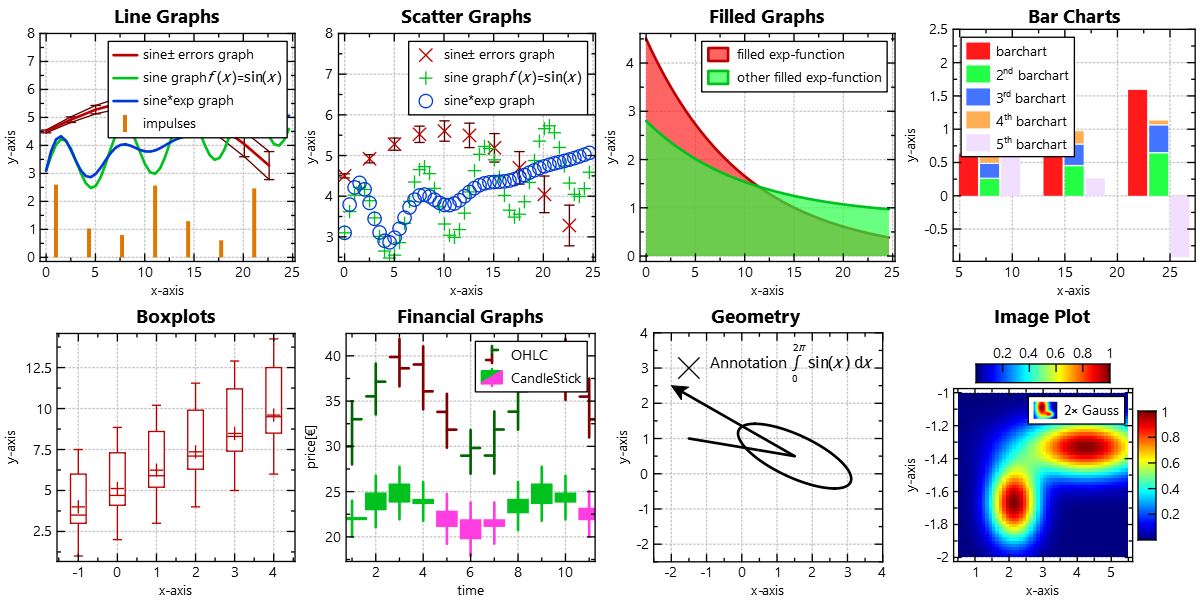
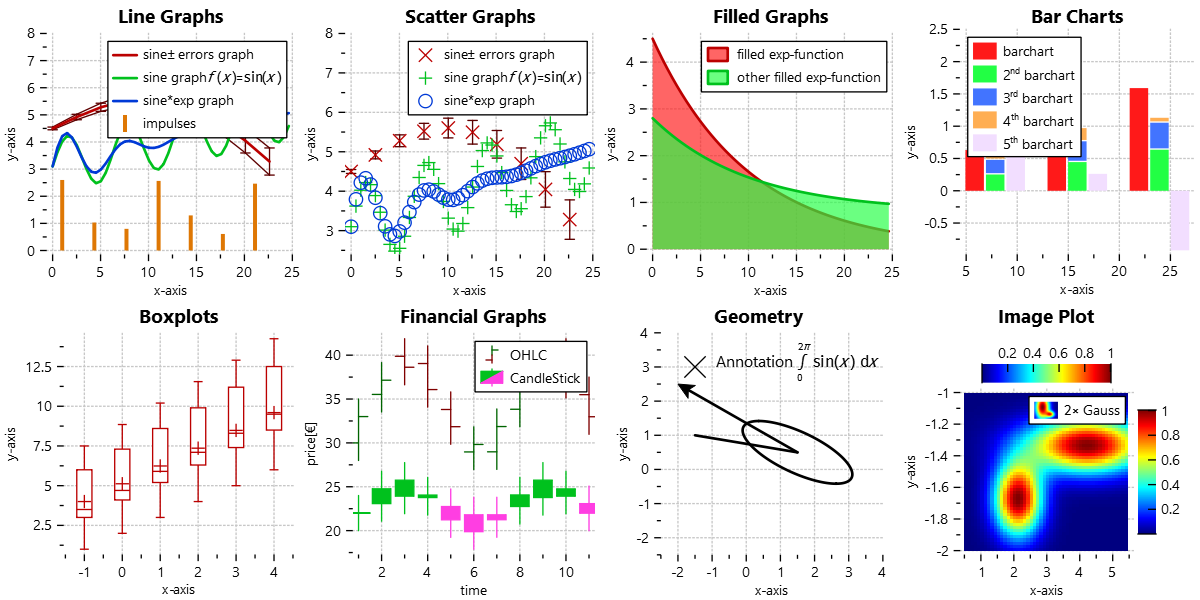
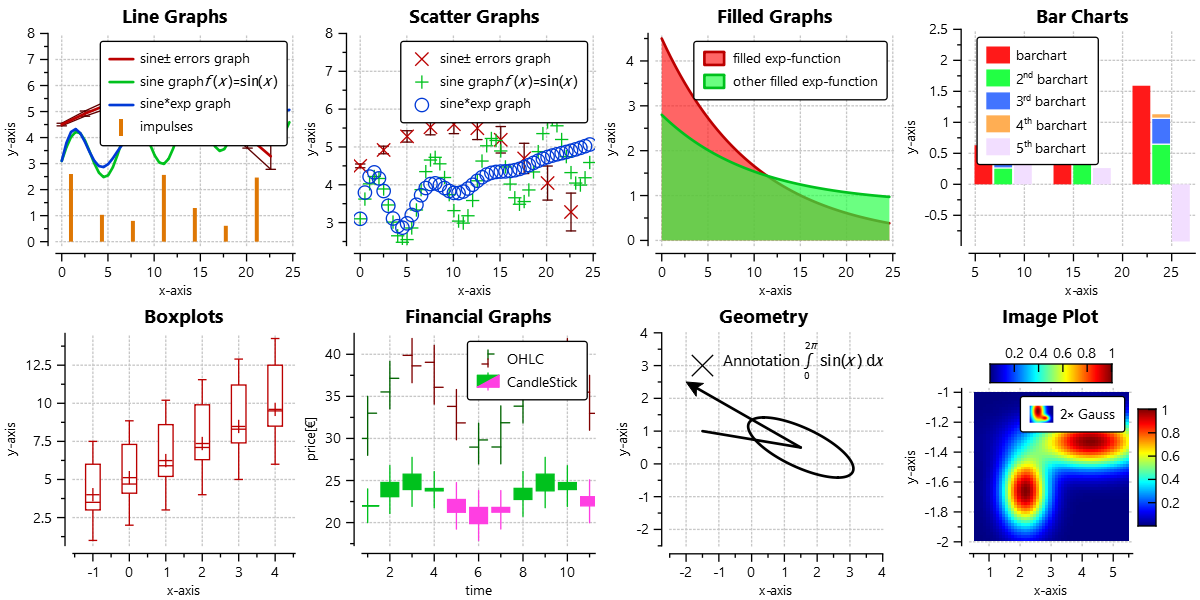
Some Example Styles
The following gallery shows a set of example styles:
Note: The styles listed above are also linked into the executable as Qt ressource ... you can use them e.g. as follows:
QSettings plotSettings(":/JKQTPlotter/styles/blackandwhite.ini", QSettings::IniFormat);;
JKQTPGetSystemDefaultStyle().loadSettings(plotSettings);
JKQTPGetSystemDefaultBaseStyle().loadSettings(plotSettings);