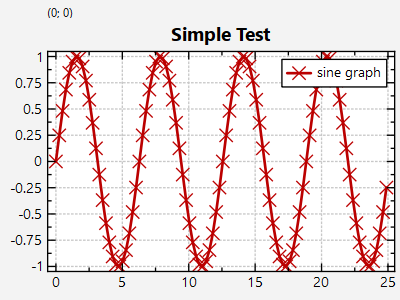
# Example (JKQTPlotter): Very simple line-graph {#JKQTPlotterSimpleTest}
This project (see `./examples/simpletest/`) simply creates a JKQTPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds a single line-graph (a sine-wave). Data is initialized from two QVector<double> objects.
The source code of the main application is (see [`jkqtplotter_simpletest.cpp`](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/tree/master/examples/simpletest/jkqtplotter_simpletest.cpp):
```.cpp
#include <QApplication>
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtplotter.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore
// (for convenience)
JKQTPlotter plot;
JKQTPDatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
// 2. now we create data for a simple plot (a sine curve)
QVector<double> X, Y;
const int Ndata=100;
for (int i=0; i<Ndata; i++) {
const double x=double(i)/double(Ndata)*8.0*M_PI;
X<<x;
Y<<sin(x);
}
// 3. make data available to JKQTPlotter by adding it to the internal
// datastore.
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise), so
// you can reuse X and Y afterwards!
// The variables columnX and columnY will contain the internal column ID
// of the newlycreated columns with names "x" and "y" and the (copied)
// data from X and Y.
size_t columnX=ds->addCopiedColumn(X, "x");
size_t columnY=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y, "y");
// 4. create a graph in the plot, which plots the dataset X/Y:
JKQTPXYLineGraph* graph1=new JKQTPXYLineGraph(&plot);
graph1->setXColumn(columnX);
graph1->setYColumn(columnY);
graph1->setTitle(QObject::tr("sine graph"));
// 5. add the graph to the plot, so it is actually displayed
plot.addGraph(graph1);
// 6. autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
plot.zoomToFit();
// show plotter and make it a decent size
plot.show();
plot.resize(600,400);
return app.exec();
}
```
The result looks like this: