reformated examples markdown-pages
549
README.md
@ -9,540 +9,17 @@ This software is licensed under the term of the GNU Lesser General Public Licens
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Examples
|
||||
This section assembles some simple examples of usage. You can find more (complex) examples for the classes in this repository in the subfolder "test". All test-projects are Qt-projects that use qmake to build. You can load them into QtCreator easily.
|
||||
|
||||
### Very simple line-graph
|
||||
This project (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest/`) simply creates a JKQtPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds a single line-graph (a sine-wave). Data is initialized from two QVector<double> objects.
|
||||
The QMake project looks like this (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest/jkqtplotter_simpletest.pro`):
|
||||
```qmake
|
||||
# source code for this simple demo
|
||||
SOURCES = jkqtplotter_simpletest.cpp
|
||||
|
||||
# configure Qt
|
||||
CONFIG += qt
|
||||
QT += core gui svg
|
||||
greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets printsupport
|
||||
|
||||
# output executable name
|
||||
TARGET = jkqtplotter_simpletest
|
||||
|
||||
# include JKQtPlotter source code
|
||||
include(../../lib/jkqtplotter.pri)
|
||||
```
|
||||
And the soruce code of the main application is (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest/jkqtplotter_simpletest.cpp`):
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <QApplication>
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtplotter.h"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QApplication app(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore
|
||||
// (for convenience)
|
||||
JKQtPlotter plot;
|
||||
JKQTPdatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. now we create data for a simple plot (a sine curve)
|
||||
QVector<double> X, Y;
|
||||
const int Ndata=100;
|
||||
for (int i=0; i<Ndata; i++) {
|
||||
const double x=double(i)/double(Ndata)*8.0*M_PI;
|
||||
X<<x;
|
||||
Y<<sin(x);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal
|
||||
// datastore.
|
||||
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise), so
|
||||
// you can reuse X and Y afterwards!
|
||||
// The variables columnX and columnY will contain the internal column ID
|
||||
// of the newlycreated columns with names "x" and "y" and the (copied)
|
||||
// data from X and Y.
|
||||
size_t columnX=ds->addCopiedColumn(X, "x");
|
||||
size_t columnY=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y, "y");
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. create a graph in the plot, which plots the dataset X/Y:
|
||||
JKQTPxyLineGraph* graph1=new JKQTPxyLineGraph(&plot);
|
||||
graph1->set_xColumn(columnX);
|
||||
graph1->set_yColumn(columnY);
|
||||
graph1->set_title(QObject::tr("sine graph"));
|
||||
|
||||
// 5. add the graph to the plot, so it is actually displayed
|
||||
plot.addGraph(graph1);
|
||||
|
||||
// 6. autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
|
||||
plot.zoomToFit();
|
||||
|
||||
// show plotter and make it a decent size
|
||||
plot.show();
|
||||
plot.resize(600,400);
|
||||
|
||||
return app.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
The result looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Simple line-graph with error bars
|
||||
This project (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_symbols_and_errors/`) simply creates a JKQtPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds a single line-graph (a sine-wave) that has y-errorbars. In addition, this example shows how to change some of the axis properties and how to use LaTeX markup to format axis labels (can actually be used for all labels in JKQtPlotter). Also, in comparison to the last example, here we initialize the data from C-type arrays (double*), instead of QVector<double> objects.
|
||||
|
||||
The soruce code of the main application is (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_symbols_and_errors/jkqtplotter_simpletest_symbols_and_errors.cpp`):
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <QApplication>
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtplotter.h"
|
||||
|
||||
// number of datapoints:
|
||||
#define Ndata 10
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QApplication app(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore (for convenience)
|
||||
JKQtPlotter plot;
|
||||
JKQTPdatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. now we create data for a simple plot (a sine curve with lin. increasing errors)
|
||||
double X[Ndata], Y[Ndata], YERROR[Ndata];
|
||||
for (int i=0; i<Ndata; i++) {
|
||||
X[i]=double(i)/double(Ndata)*2.0*M_PI;
|
||||
Y[i]=sin(X[i]);
|
||||
YERROR[i]=0.2+double(i)/double(Ndata)*0.25;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal datastore.
|
||||
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise), so you can
|
||||
// reuse X and Y afterwards!
|
||||
// the variables columnX and columnY will contain the internal column ID of the newly
|
||||
// created columns with names "x" and "y" and the (copied) data from X and Y.
|
||||
size_t columnX=ds->addCopiedColumn(X, Ndata, "x");
|
||||
size_t columnY=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y, Ndata, "y");
|
||||
size_t columnYE=ds->addCopiedColumn(YERROR, Ndata, "y-error");
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. create a graph in the plot, which plots the dataset X/Y:
|
||||
JKQTPxyLineErrorGraph* graph1=new JKQTPxyLineErrorGraph(&plot);
|
||||
graph1->set_xColumn(columnX);
|
||||
graph1->set_yColumn(columnY);
|
||||
graph1->set_yErrorColumn(columnYE);
|
||||
graph1->set_symbol(JKQTPfilledStar); // set symbol style
|
||||
graph1->set_yErrorStyle(JKQTPerrorBars); // set error indicator type
|
||||
graph1->set_drawLine(false); // don't draw a line
|
||||
graph1->set_title(QObject::tr("sine graph"));
|
||||
|
||||
// 5. add the graph to the plot, so it is actually displayed
|
||||
plot.addGraph(graph1);
|
||||
|
||||
// 6. hide 0-lines
|
||||
plot.getXAxis()->set_showZeroAxis(false);
|
||||
plot.getYAxis()->set_showZeroAxis(false);
|
||||
|
||||
// 7. set some axis properties (we use LaTeX for nice equation rendering)
|
||||
plot.getXAxis()->set_axisLabel(QObject::tr("x-axis $x$ [mm]"));
|
||||
plot.getYAxis()->set_axisLabel(QObject::tr("\\textbf{\\color{red}{y-axis} $\\left(y=\\sin(x)\\pm(0.2+0.25\\cdot x)\\right)$ [A.U.]}"));
|
||||
plot.getXAxis()->set_labelFont("Arial");
|
||||
plot.getYAxis()->set_labelFont("Times New Roman");
|
||||
plot.getYAxis()->set_labelFontSize(12); // large x-axis label
|
||||
plot.getYAxis()->set_tickLabelFontSize(10); // and larger y-axis tick labels
|
||||
|
||||
// 8. autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
|
||||
plot.zoomToFit();
|
||||
|
||||
// show plotter and make it a decent size
|
||||
plot.show();
|
||||
plot.resize(600,400);
|
||||
|
||||
return app.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
The result looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Simple barchart
|
||||
This project (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_barchart/`) simply creates a JKQtPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds several barcharts. They are ordered in groups.
|
||||
|
||||
The soruce code of the main application is (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_barchart/jkqtplotter_simpletest_barchart.cpp`):
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <QApplication>
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtplotter.h"
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtpbarchartelements.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#define Ndata 5
|
||||
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QApplication app(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore (for convenience)
|
||||
JKQtPlotter plot;
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForGraphs(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForSystem(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForText(true); // nicer (but slower) text rendering
|
||||
JKQTPdatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. now we create data for three simple barchart
|
||||
QString L[Ndata]={ "cat. A", "cat. B", "cat. C", "cat. D", "other"};
|
||||
double X[Ndata]={ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
|
||||
double Y1[Ndata]={ 5, 4, 3, 4, 5};
|
||||
double Y2[Ndata]={ -5, -3, 1, 3, 6};
|
||||
double Y3[Ndata]={ 6, 2, 5, 3, 6};
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal datastore.
|
||||
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise)
|
||||
// the variables columnX and columnY... will contain the internal column ID of the
|
||||
// newly created columns with names "x" and "y..." and the (copied) data from X
|
||||
// and Y...
|
||||
size_t columnX=ds->addCopiedColumn(X, Ndata, "x");
|
||||
size_t columnY1=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y1, Ndata, "y1");
|
||||
size_t columnY2=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y2, Ndata, "y2");
|
||||
size_t columnY3=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y3, Ndata, "y3");
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. create graphs in the plot, which plots the dataset X/Y1, X/Y2 and X/Y3:
|
||||
JKQTPbarVerticalGraph* graph1=new JKQTPbarVerticalGraph(&plot);
|
||||
graph1->set_xColumn(columnX);
|
||||
graph1->set_yColumn(columnY1);
|
||||
graph1->set_title(QObject::tr("dataset 1"));
|
||||
JKQTPbarVerticalGraph* graph2=new JKQTPbarVerticalGraph(&plot);
|
||||
graph2->set_xColumn(columnX);
|
||||
graph2->set_yColumn(columnY2);
|
||||
graph2->set_title(QObject::tr("dataset 2"));
|
||||
JKQTPbarVerticalGraph* graph3=new JKQTPbarVerticalGraph(&plot);
|
||||
graph3->set_xColumn(columnX);
|
||||
graph3->set_yColumn(columnY3);
|
||||
graph3->set_title(QObject::tr("dataset 3"));
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 5. add the graphs to the plot, so it is actually displayed
|
||||
plot.addGraph(graph1);
|
||||
plot.addGraph(graph2);
|
||||
plot.addGraph(graph3);
|
||||
|
||||
// 6. now we set the graphs, so they are plotted side-by-side
|
||||
// This function searches all JKQTPbarVerticalGraph in the current
|
||||
// plot and sets their shift/scale so they form a nice plot with
|
||||
// side-by-side groups
|
||||
graph1->autoscaleBarWidthAndShift(0.75, 1);
|
||||
|
||||
// 7. data is grouped into 5 numbere groups (1..5), but we also have string
|
||||
// labels for these groups (stored in L). In order to display these labels,
|
||||
// we have to tell the x-Axis to use these special labels:
|
||||
plot.getXAxis()->addAxisTickLabels(X, L, Ndata);
|
||||
// also we can rotate the labels a bit (by 45 degree), so they fit better
|
||||
plot.getXAxis()->set_tickLabelAngle(45);
|
||||
plot.getXAxis()->set_tickLabelFontSize(12);
|
||||
|
||||
// 8. finally we move the plot key/legend to the outside, top-right
|
||||
// and lay it out as a single row
|
||||
// NOTE: plot is a descendent of QWidget, which uses an internal object of
|
||||
// type JKQTBasePlotter, which does the actual plotting.
|
||||
// So many properties of the plot are only available in this internal
|
||||
// object, which you can access by plot.get_plotter().
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_keyPosition(JKQTPkeyOutsideTopRight);
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_keyLayout(JKQTPkeyLayoutOneRow);
|
||||
|
||||
// 9 autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
|
||||
plot.zoomToFit();
|
||||
|
||||
// show plotter and make it a decent size
|
||||
plot.show();
|
||||
plot.resize(600,400);
|
||||
|
||||
return app.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
The result looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Simple stacked barchart
|
||||
This project (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_stackedbars/`) simply creates a JKQtPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds several stacked barcharts.
|
||||
|
||||
The soruce code of the main application is (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_stackedbars/jkqtplotter_simpletest_stackedbars.cpp`):
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <QApplication>
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtplotter.h"
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtpbarchartelements.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#define Ndata 5
|
||||
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QApplication app(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore (for convenience)
|
||||
JKQtPlotter plot;
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForGraphs(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForSystem(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForText(true); // nicer (but slower) text rendering
|
||||
JKQTPdatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. now we create data for the charts (taken from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Energiemix_Deutschland.svg)
|
||||
QVector<double> year, percentage_other, percentage_coaloil, percentage_gas, percentage_nuclear, percentage_green;
|
||||
year << 1990 << 1995 << 2000 << 2005 << 2010 << 2015;
|
||||
percentage_other << 3.5 << 3.5 << 4.4 << 4.4 << 5 << 5 ;
|
||||
percentage_coaloil << 58.7 << 55.7 << 51.5 << 48.2 << 42.9 << 43.1;
|
||||
percentage_gas << 6.5 << 7.7 << 8.5 << 11.7 << 14.1 << 9.6 ;
|
||||
percentage_nuclear << 27.7 << 28.7 << 29.4 << 26.2 << 22.2 << 14.2;
|
||||
percentage_green << 3.6 << 4.4 << 6.2 << 9.5 << 15.8 << 28.1;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal datastore.
|
||||
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise)
|
||||
// the variables cYear, cOther ... will contain the internal column ID of the
|
||||
// newly created columns with names "year" and "other" ... and the (copied) data
|
||||
size_t cYear=ds->addCopiedColumn(year, "year");
|
||||
size_t cOther=ds->addCopiedColumn(percentage_other, "other");
|
||||
size_t cCoalOil=ds->addCopiedColumn(percentage_coaloil, "coal & oil");
|
||||
size_t cGas=ds->addCopiedColumn(percentage_gas, "natural gas");
|
||||
size_t cNuclear=ds->addCopiedColumn(percentage_nuclear, "nuclear energy");
|
||||
size_t cGreen=ds->addCopiedColumn(percentage_green, "green energy");
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. create graphs in the plot, which plots the dataset year/other, year/coal, ...
|
||||
// The color of the graphs is set by calling set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(), which sets the
|
||||
// fillColor to the given color and makes the outline of the bars (i.e. their "color") a darker
|
||||
// shade of the given color.
|
||||
QVector<JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph*> graphs;
|
||||
graphs.push_back(new JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph(&plot));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_xColumn(cYear);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_yColumn(cOther);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_title(QObject::tr("other sources"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(QColor("red"));
|
||||
graphs.push_back(new JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph(&plot));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_xColumn(cYear);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_yColumn(cCoalOil);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_title(QObject::tr("coal & oil"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(QColor("darkgrey"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->stackUpon(graphs[graphs.size()-2]);
|
||||
graphs.push_back(new JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph(&plot));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_xColumn(cYear);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_yColumn(cGas);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_title(QObject::tr("natural gas"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(QColor("blue"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->stackUpon(graphs[graphs.size()-2]);
|
||||
graphs.push_back(new JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph(&plot));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_xColumn(cYear);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_yColumn(cNuclear);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_title(QObject::tr("nuclear energy"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(QColor("gold"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->stackUpon(graphs[graphs.size()-2]);
|
||||
graphs.push_back(new JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph(&plot));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_xColumn(cYear);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_yColumn(cGreen);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_title(QObject::tr("green energy"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(QColor("darkgreen"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->stackUpon(graphs[graphs.size()-2]);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 5. add the graphs to the plot, so it is actually displayed
|
||||
plot.addGraphs(graphs);
|
||||
|
||||
// 6. set axis labels
|
||||
plot.get_xAxis()->set_axisLabel("year");
|
||||
plot.get_yAxis()->set_axisLabel("fraction of energy production in Germany [%]");
|
||||
|
||||
// 7. finally we move the plot key/legend to the outside, top-right
|
||||
// and lay it out as a single row
|
||||
// NOTE: plot is a descendent of QWidget, which uses an internal object of
|
||||
// type JKQTBasePlotter, which does the actual plotting.
|
||||
// So many properties of the plot are only available in this internal
|
||||
// object, which you can access by plot.get_plotter().
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_keyPosition(JKQTPkeyOutsideTopRight);
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_keyLayout(JKQTPkeyLayoutOneRow);
|
||||
|
||||
// 8 autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
|
||||
plot.zoomToFit();
|
||||
|
||||
// show plotter and make it a decent size
|
||||
plot.show();
|
||||
plot.resize(600,400);
|
||||
|
||||
return app.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
The result looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
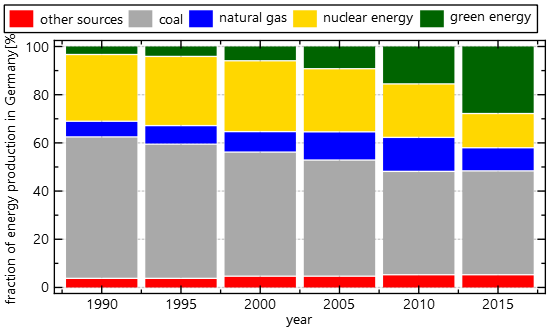
|
||||
|
||||
If you use `JKQTPbarHorizontalGraphStacked` instead of `JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph`, you'll get a result like this:
|
||||
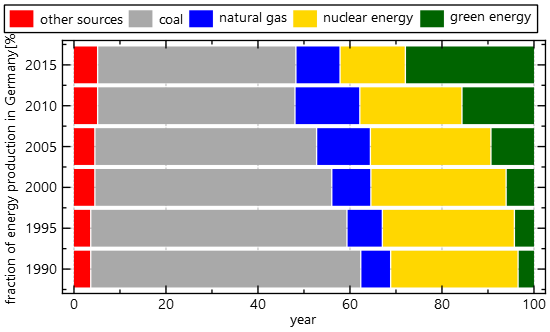
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Simple math image plot
|
||||
This project (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_imageplot/`) simply creates a JKQtPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds a color-coded image plot of a mathematical function (here the Airy disk). The image is stored as a simple C-array in row-major ordering and then copied into a single column of the internal datasdtore (JKQTPMathImage could be directly used without the internal datastore). This very simple interface can also be used to interface with many common image processing libraries, like CImg or OpenCV.
|
||||
|
||||
The soruce code of the main application is (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_imageplot/jkqtplotter_simpletest_imageplot.cpp`):
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <QApplication>
|
||||
#include <cmath>
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtplotter.h"
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtpimageelements.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef M_PI
|
||||
#define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QApplication app(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
JKQtPlotter plot;
|
||||
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore (for convenience)
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForGraphs(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForSystem(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForText(true); // nicer (but slower) text rendering
|
||||
JKQTPdatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. now we create data for the charts (taken from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Energiemix_Deutschland.svg)
|
||||
const int NX=100; // image dimension in x-direction [pixels]
|
||||
const int NY=100; // image dimension in x-direction [pixels]
|
||||
const double dx=1e-2; // size of a pixel in x-direction [micrometers]
|
||||
const double dy=1e-2; // size of a pixel in x-direction [micrometers]
|
||||
const double w=static_cast<double>(NX)*dx;
|
||||
const double h=static_cast<double>(NY)*dy;
|
||||
double airydisk[NX*NY]; // row-major image
|
||||
|
||||
// 2.1 Parameters for airy disk plot (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Airy_disk)
|
||||
double NA=1.1; // numerical aperture of lens
|
||||
double wavelength=488e-3; // wavelength of the light [micrometers]
|
||||
|
||||
// 2.2 calculate image of airy disk in a row-major array
|
||||
double x, y=-h/2.0;
|
||||
for (int iy=0; iy<NY; iy++ ) {
|
||||
x=-w/2.0;
|
||||
for (int ix=0; ix<NX; ix++ ) {
|
||||
const double r=sqrt(x*x+y*y);
|
||||
const double v=2.0*M_PI*NA*r/wavelength;
|
||||
airydisk[iy*NX+ix] = pow(2.0*j1(v)/v, 2);
|
||||
x+=dx;
|
||||
}
|
||||
y+=dy;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal datastore.
|
||||
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise)
|
||||
// the variables cYear, cOther ... will contain the internal column ID of the
|
||||
// newly created columns with names "year" and "other" ... and the (copied) data
|
||||
size_t cAiryDisk=ds->addCopiedImageAsColumn(airydisk, NX, NY, "imagedata");
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. create graphs in the plot, which plots the dataset year/other, year/coal, ...
|
||||
// The color of the graphs is set by calling set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(), which sets the
|
||||
// fillColor to the given color and makes the outline of the bars (i.e. their "color") a darker
|
||||
// shade of the given color.
|
||||
JKQTPColumnMathImage* graph=new JKQTPColumnMathImage(&plot);
|
||||
graph->set_title("");
|
||||
graph->set_imageColumn(cAiryDisk);
|
||||
graph->set_Nx(NX);
|
||||
graph->set_Ny(NY);
|
||||
graph->set_x(-w/2.0);
|
||||
graph->set_y(-h/2.0);
|
||||
graph->set_width(w);
|
||||
graph->set_height(h);
|
||||
graph->set_palette(JKQTPMathImageMATLAB); // color-map is "MATLAB"
|
||||
graph->get_colorBarRightAxis()->set_axisLabel("light intensity [A.U.]"); // get coordinate axis of color-bar and set its label
|
||||
|
||||
// 5. add the graphs to the plot, so it is actually displayed
|
||||
plot.addGraph(graph);
|
||||
|
||||
// 6. set axis labels
|
||||
plot.get_xAxis()->set_axisLabel("x [{\\mu}m]");
|
||||
plot.get_yAxis()->set_axisLabel("y [{\\mu}m]");
|
||||
|
||||
// 7. fix axis and plot aspect ratio to 1
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_maintainAspectRatio(true);
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_maintainAxisAspectRatio(true);
|
||||
|
||||
// 8 autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
|
||||
plot.zoomToFit();
|
||||
|
||||
// show plotter and make it a decent size
|
||||
plot.show();
|
||||
plot.resize(600,600);
|
||||
plot.setWindowTitle("JKQTPColumnMathImage");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return app.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
The result looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/master/test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_imageplot_opencv)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# JKQTmathText
|
||||
JKQTmathText is a hand-written LaTeX-renderer for Qt (implemented in native C++, using Qt). It supports a large set of standard LaTeX markup and can render it to a QPainter.
|
||||
## A simple usage example
|
||||
This project (see `./test/jkqtmathtext_simpletest/`) simply creates a QLabel (as a new window) that displays a rendered LaTeX equation (here the time-dependent Schrödinger equation).
|
||||
The QMake project looks like this (see `./test/jkqtmathtext_simpletest/jkqtmathtext_simpletest.pro`):
|
||||
```qmake
|
||||
# include JKQTmathText source-code, including the open-source XITS fonts
|
||||
include(../../lib/jkqtmathtext_with_xits.pri)
|
||||
SOURCES += jkqtmathtext_simpletest.cpp
|
||||
|
||||
# if you don't want to use the XITS fonts, use this line (and uncomment the
|
||||
# last two line!):
|
||||
#include(../../lib/jkqtmathtext.pri)
|
||||
|
||||
CONFIG += qt
|
||||
QT += core gui
|
||||
greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets printsupport
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET = jkqtmathtext_simpletest
|
||||
```
|
||||
And the soruce code of the main application is (see `./test/jkqtmathtext_simpletest/jkqtmathtext_simpletest.cpp`):
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <QApplication>
|
||||
#include <QLabel>
|
||||
#include <QPixmap>
|
||||
#include "jkqtmathtext/jkqtmathtext.h"
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QApplication app(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
// we use a simple label to display the math text
|
||||
QLabel lab;
|
||||
|
||||
// 1. we will paint into a QPixmap
|
||||
QPixmap pix(600,400);
|
||||
pix.fill(QColor("white"));
|
||||
QPainter painter;
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. now we create a JKQTmathText object.
|
||||
// Also we configure the JKQTmathText to use the XITS fonts that
|
||||
// were included in the *.pro-file
|
||||
JKQTmathText mathText;
|
||||
mathText.useXITS();
|
||||
mathText.set_fontSize(20);
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. now we parse some LaTeX code (the Schroedinger's equation), so
|
||||
// we can draw it onto the QPixmap in the next step
|
||||
mathText.parse("$\\left[-\\frac{\\hbar^2}{2m}\\frac{\\partial^2}{\\partial x^2}+V(x)\\right]\\Psi(x)=\\mathrm{i}\\hbar\\frac{\\partial}{\\partial t}\\Psi(x)$");
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. here we do the painting
|
||||
painter.begin(&pix);
|
||||
mathText.draw(painter, Qt::AlignCenter, QRectF(0,0,pix.width(), pix.height()), false);
|
||||
painter.end();
|
||||
|
||||
// now we display and resize the label as a window
|
||||
lab.setPixmap(pix);
|
||||
lab.show();
|
||||
lab.resize(600,400);
|
||||
|
||||
return app.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
The result looks like this:
|
||||

|
||||
This section assembles some simple examples of usage.
|
||||
You can find more (complex) examples for the classes in this repository in the subfolder "test".
|
||||
All test-projects are Qt-projects that use qmake to build. You can load them into QtCreator easily.
|
||||
|
||||
Choose an example from the list below:
|
||||
|
||||
[ Very Basic Example (Line Graph)](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/tree/master/test/jkqtmathtext_simpletest)
|
||||
[ Simple Line/Symbol Graph With Errorbars](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/tree/master/test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_symbols_and_errors)
|
||||
[ Simple Bar Charts](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/tree/master/test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_barchart)
|
||||
[ Stacked Bar Charts](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/tree/master/test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_stackedbars)
|
||||
[ Raw C Image Plot](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/tree/master/test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_imageplot)
|
||||
[ OpenCV Image Plot](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/tree/master/test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_imageplot_opencv)
|
||||
[ JKQTMathText (LaTeX Renderer)](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/tree/master/test/jkqtmathtext_simpletest)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
BIN
screenshots/JKQTPbarHorizontalGraphStacked_small.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 9.4 KiB |
BIN
screenshots/JKQTPbarVerticalGraphStacked_small.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 9.1 KiB |
BIN
screenshots/jkqtmathtext_simpletest_small.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 6.6 KiB |
BIN
screenshots/jkqtplotter_simpletest1_small.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 15 KiB |
BIN
screenshots/jkqtplotter_simpletest_barchart_small.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 11 KiB |
BIN
screenshots/jkqtplotter_simpletest_imageplot_small.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 13 KiB |
BIN
screenshots/jkqtplotter_simpletest_symbols_and_errors_small.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 12 KiB |
72
test/jkqtmathtext_simpletest/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
[Back to JKQTPlotter main page](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/)
|
||||
|
||||
# JKQtPlotter
|
||||
|
||||
## JKQTmathText
|
||||
JKQTmathText is a hand-written LaTeX-renderer for Qt (implemented in native C++, using Qt). It supports a large set of standard LaTeX markup and can render it to a QPainter.
|
||||
## A simple usage example
|
||||
This project (see `./test/jkqtmathtext_simpletest/`) simply creates a QLabel (as a new window) that displays a rendered LaTeX equation (here the time-dependent Schrödinger equation).
|
||||
The QMake project looks like this (see `./test/jkqtmathtext_simpletest/jkqtmathtext_simpletest.pro`):
|
||||
```qmake
|
||||
# include JKQTmathText source-code, including the open-source XITS fonts
|
||||
include(../../lib/jkqtmathtext_with_xits.pri)
|
||||
SOURCES += jkqtmathtext_simpletest.cpp
|
||||
|
||||
# if you don't want to use the XITS fonts, use this line (and uncomment the
|
||||
# last two line!):
|
||||
#include(../../lib/jkqtmathtext.pri)
|
||||
|
||||
CONFIG += qt
|
||||
QT += core gui
|
||||
greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets printsupport
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET = jkqtmathtext_simpletest
|
||||
```
|
||||
And the soruce code of the main application is (see `./test/jkqtmathtext_simpletest/jkqtmathtext_simpletest.cpp`):
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <QApplication>
|
||||
#include <QLabel>
|
||||
#include <QPixmap>
|
||||
#include "jkqtmathtext/jkqtmathtext.h"
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QApplication app(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
// we use a simple label to display the math text
|
||||
QLabel lab;
|
||||
|
||||
// 1. we will paint into a QPixmap
|
||||
QPixmap pix(600,400);
|
||||
pix.fill(QColor("white"));
|
||||
QPainter painter;
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. now we create a JKQTmathText object.
|
||||
// Also we configure the JKQTmathText to use the XITS fonts that
|
||||
// were included in the *.pro-file
|
||||
JKQTmathText mathText;
|
||||
mathText.useXITS();
|
||||
mathText.set_fontSize(20);
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. now we parse some LaTeX code (the Schroedinger's equation), so
|
||||
// we can draw it onto the QPixmap in the next step
|
||||
mathText.parse("$\\left[-\\frac{\\hbar^2}{2m}\\frac{\\partial^2}{\\partial x^2}+V(x)\\right]\\Psi(x)=\\mathrm{i}\\hbar\\frac{\\partial}{\\partial t}\\Psi(x)$");
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. here we do the painting
|
||||
painter.begin(&pix);
|
||||
mathText.draw(painter, Qt::AlignCenter, QRectF(0,0,pix.width(), pix.height()), false);
|
||||
painter.end();
|
||||
|
||||
// now we display and resize the label as a window
|
||||
lab.setPixmap(pix);
|
||||
lab.show();
|
||||
lab.resize(600,400);
|
||||
|
||||
return app.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
The result looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Back to JKQTPlotter main page](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/)
|
||||
82
test/jkqtplotter_simpletest/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
|
||||
[Back to JKQTPlotter main page](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/)
|
||||
|
||||
# JKQtPlotter
|
||||
|
||||
## Very simple line-graph
|
||||
This project (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest/`) simply creates a JKQtPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds a single line-graph (a sine-wave). Data is initialized from two QVector<double> objects.
|
||||
The QMake project looks like this (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest/jkqtplotter_simpletest.pro`):
|
||||
```qmake
|
||||
# source code for this simple demo
|
||||
SOURCES = jkqtplotter_simpletest.cpp
|
||||
|
||||
# configure Qt
|
||||
CONFIG += qt
|
||||
QT += core gui svg
|
||||
greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets printsupport
|
||||
|
||||
# output executable name
|
||||
TARGET = jkqtplotter_simpletest
|
||||
|
||||
# include JKQtPlotter source code
|
||||
include(../../lib/jkqtplotter.pri)
|
||||
```
|
||||
And the soruce code of the main application is (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest/jkqtplotter_simpletest.cpp`):
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <QApplication>
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtplotter.h"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QApplication app(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore
|
||||
// (for convenience)
|
||||
JKQtPlotter plot;
|
||||
JKQTPdatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. now we create data for a simple plot (a sine curve)
|
||||
QVector<double> X, Y;
|
||||
const int Ndata=100;
|
||||
for (int i=0; i<Ndata; i++) {
|
||||
const double x=double(i)/double(Ndata)*8.0*M_PI;
|
||||
X<<x;
|
||||
Y<<sin(x);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal
|
||||
// datastore.
|
||||
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise), so
|
||||
// you can reuse X and Y afterwards!
|
||||
// The variables columnX and columnY will contain the internal column ID
|
||||
// of the newlycreated columns with names "x" and "y" and the (copied)
|
||||
// data from X and Y.
|
||||
size_t columnX=ds->addCopiedColumn(X, "x");
|
||||
size_t columnY=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y, "y");
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. create a graph in the plot, which plots the dataset X/Y:
|
||||
JKQTPxyLineGraph* graph1=new JKQTPxyLineGraph(&plot);
|
||||
graph1->set_xColumn(columnX);
|
||||
graph1->set_yColumn(columnY);
|
||||
graph1->set_title(QObject::tr("sine graph"));
|
||||
|
||||
// 5. add the graph to the plot, so it is actually displayed
|
||||
plot.addGraph(graph1);
|
||||
|
||||
// 6. autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
|
||||
plot.zoomToFit();
|
||||
|
||||
// show plotter and make it a decent size
|
||||
plot.show();
|
||||
plot.resize(600,400);
|
||||
|
||||
return app.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
The result looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[Back to JKQTPlotter main page](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/)
|
||||
101
test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_barchart/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
[Back to JKQTPlotter main page](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/)
|
||||
|
||||
# JKQtPlotter
|
||||
|
||||
## Simple barchart
|
||||
This project (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_barchart/`) simply creates a JKQtPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds several barcharts. They are ordered in groups.
|
||||
|
||||
The soruce code of the main application is (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_barchart/jkqtplotter_simpletest_barchart.cpp`):
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <QApplication>
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtplotter.h"
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtpbarchartelements.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#define Ndata 5
|
||||
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QApplication app(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore (for convenience)
|
||||
JKQtPlotter plot;
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForGraphs(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForSystem(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForText(true); // nicer (but slower) text rendering
|
||||
JKQTPdatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. now we create data for three simple barchart
|
||||
QString L[Ndata]={ "cat. A", "cat. B", "cat. C", "cat. D", "other"};
|
||||
double X[Ndata]={ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
|
||||
double Y1[Ndata]={ 5, 4, 3, 4, 5};
|
||||
double Y2[Ndata]={ -5, -3, 1, 3, 6};
|
||||
double Y3[Ndata]={ 6, 2, 5, 3, 6};
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal datastore.
|
||||
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise)
|
||||
// the variables columnX and columnY... will contain the internal column ID of the
|
||||
// newly created columns with names "x" and "y..." and the (copied) data from X
|
||||
// and Y...
|
||||
size_t columnX=ds->addCopiedColumn(X, Ndata, "x");
|
||||
size_t columnY1=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y1, Ndata, "y1");
|
||||
size_t columnY2=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y2, Ndata, "y2");
|
||||
size_t columnY3=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y3, Ndata, "y3");
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. create graphs in the plot, which plots the dataset X/Y1, X/Y2 and X/Y3:
|
||||
JKQTPbarVerticalGraph* graph1=new JKQTPbarVerticalGraph(&plot);
|
||||
graph1->set_xColumn(columnX);
|
||||
graph1->set_yColumn(columnY1);
|
||||
graph1->set_title(QObject::tr("dataset 1"));
|
||||
JKQTPbarVerticalGraph* graph2=new JKQTPbarVerticalGraph(&plot);
|
||||
graph2->set_xColumn(columnX);
|
||||
graph2->set_yColumn(columnY2);
|
||||
graph2->set_title(QObject::tr("dataset 2"));
|
||||
JKQTPbarVerticalGraph* graph3=new JKQTPbarVerticalGraph(&plot);
|
||||
graph3->set_xColumn(columnX);
|
||||
graph3->set_yColumn(columnY3);
|
||||
graph3->set_title(QObject::tr("dataset 3"));
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 5. add the graphs to the plot, so it is actually displayed
|
||||
plot.addGraph(graph1);
|
||||
plot.addGraph(graph2);
|
||||
plot.addGraph(graph3);
|
||||
|
||||
// 6. now we set the graphs, so they are plotted side-by-side
|
||||
// This function searches all JKQTPbarVerticalGraph in the current
|
||||
// plot and sets their shift/scale so they form a nice plot with
|
||||
// side-by-side groups
|
||||
graph1->autoscaleBarWidthAndShift(0.75, 1);
|
||||
|
||||
// 7. data is grouped into 5 numbere groups (1..5), but we also have string
|
||||
// labels for these groups (stored in L). In order to display these labels,
|
||||
// we have to tell the x-Axis to use these special labels:
|
||||
plot.getXAxis()->addAxisTickLabels(X, L, Ndata);
|
||||
// also we can rotate the labels a bit (by 45 degree), so they fit better
|
||||
plot.getXAxis()->set_tickLabelAngle(45);
|
||||
plot.getXAxis()->set_tickLabelFontSize(12);
|
||||
|
||||
// 8. finally we move the plot key/legend to the outside, top-right
|
||||
// and lay it out as a single row
|
||||
// NOTE: plot is a descendent of QWidget, which uses an internal object of
|
||||
// type JKQTBasePlotter, which does the actual plotting.
|
||||
// So many properties of the plot are only available in this internal
|
||||
// object, which you can access by plot.get_plotter().
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_keyPosition(JKQTPkeyOutsideTopRight);
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_keyLayout(JKQTPkeyLayoutOneRow);
|
||||
|
||||
// 9 autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
|
||||
plot.zoomToFit();
|
||||
|
||||
// show plotter and make it a decent size
|
||||
plot.show();
|
||||
plot.resize(600,400);
|
||||
|
||||
return app.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
The result looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[Back to JKQTPlotter main page](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/)
|
||||
123
test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_imageplot/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
||||
[Back to JKQTPlotter main page](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/)
|
||||
|
||||
# JKQtPlotter
|
||||
|
||||
## Simple math image plot
|
||||
This project (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_imageplot/`) simply creates a JKQtPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds a color-coded image plot of a mathematical function (here the Airy disk). The image is stored as a simple C-array in row-major ordering and then copied into a single column of the internal datasdtore (JKQTPMathImage could be directly used without the internal datastore). This very simple interface can also be used to interface with many common image processing libraries, like CImg or OpenCV.
|
||||
|
||||
The soruce code of the main application is (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_imageplot/jkqtplotter_simpletest_imageplot.cpp`):
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <QApplication>
|
||||
#include <cmath>
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtplotter.h"
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtpimageelements.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef M_PI
|
||||
#define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QApplication app(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
JKQtPlotter plot;
|
||||
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore (for convenience)
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForGraphs(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForSystem(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForText(true); // nicer (but slower) text rendering
|
||||
JKQTPdatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. now we create data for the charts (taken from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Energiemix_Deutschland.svg)
|
||||
const int NX=100; // image dimension in x-direction [pixels]
|
||||
const int NY=100; // image dimension in x-direction [pixels]
|
||||
const double dx=1e-2; // size of a pixel in x-direction [micrometers]
|
||||
const double dy=1e-2; // size of a pixel in x-direction [micrometers]
|
||||
const double w=static_cast<double>(NX)*dx;
|
||||
const double h=static_cast<double>(NY)*dy;
|
||||
double airydisk[NX*NY]; // row-major image
|
||||
|
||||
// 2.1 Parameters for airy disk plot (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Airy_disk)
|
||||
double NA=1.1; // numerical aperture of lens
|
||||
double wavelength=488e-3; // wavelength of the light [micrometers]
|
||||
|
||||
// 2.2 calculate image of airy disk in a row-major array
|
||||
double x, y=-h/2.0;
|
||||
for (int iy=0; iy<NY; iy++ ) {
|
||||
x=-w/2.0;
|
||||
for (int ix=0; ix<NX; ix++ ) {
|
||||
const double r=sqrt(x*x+y*y);
|
||||
const double v=2.0*M_PI*NA*r/wavelength;
|
||||
airydisk[iy*NX+ix] = pow(2.0*j1(v)/v, 2);
|
||||
x+=dx;
|
||||
}
|
||||
y+=dy;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal datastore.
|
||||
// In this step the contents of C-array airydisk is copied into a column
|
||||
// of the datastore in row-major order
|
||||
size_t cAiryDisk=ds->addCopiedImageAsColumn(airydisk, NX, NY, "imagedata");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. create a graph (JKQTPColumnMathImage) with the column created above as data
|
||||
// The data is color-coded with the color-palette JKQTPMathImageMATLAB
|
||||
// the converted range of data is determined automatically because set_autoImageRange(true)
|
||||
JKQTPColumnMathImage* graph=new JKQTPColumnMathImage(&plot);
|
||||
graph->set_title("");
|
||||
// image column with the data
|
||||
graph->set_imageColumn(cAiryDisk);
|
||||
// set size of the data (the datastore does not contain this info, as it only manages 1D columns of data and this is used to assume a row-major ordering
|
||||
graph->set_Nx(NX);
|
||||
graph->set_Ny(NY);
|
||||
// where does the image start in the plot, given in plot-axis-coordinates (bottom-left corner)
|
||||
graph->set_x(-w/2.0);
|
||||
graph->set_y(-h/2.0);
|
||||
// width and height of the image in plot-axis-coordinates
|
||||
graph->set_width(w);
|
||||
graph->set_height(h);
|
||||
// color-map is "MATLAB"
|
||||
graph->set_palette(JKQTPMathImageMATLAB);
|
||||
// get coordinate axis of color-bar and set its label
|
||||
graph->get_colorBarRightAxis()->set_axisLabel("light intensity [A.U.]");
|
||||
// determine min/max of data automatically and use it to set the range of the color-scale
|
||||
graph->set_autoImageRange(true);
|
||||
// you can set the color-scale range manually by using:
|
||||
// graph->set_autoImageRange(false);
|
||||
// graph->set_imageMin(0);
|
||||
// graph->set_imageMax(10);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 5. add the graphs to the plot, so it is actually displayed
|
||||
plot.addGraph(graph);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 6. set axis labels
|
||||
plot.get_xAxis()->set_axisLabel("x [{\\mu}m]");
|
||||
plot.get_yAxis()->set_axisLabel("y [{\\mu}m]");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 7. fix axis and plot aspect ratio to 1
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_maintainAspectRatio(true);
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_maintainAxisAspectRatio(true);
|
||||
|
||||
// 8 autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
|
||||
plot.zoomToFit();
|
||||
|
||||
// show plotter and make it a decent size
|
||||
plot.show();
|
||||
plot.resize(600,600);
|
||||
plot.setWindowTitle("JKQTPColumnMathImage");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return app.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
The result looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Back to JKQTPlotter main page](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/)
|
||||
@ -48,34 +48,48 @@ int main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal datastore.
|
||||
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise)
|
||||
// the variables cYear, cOther ... will contain the internal column ID of the
|
||||
// newly created columns with names "year" and "other" ... and the (copied) data
|
||||
// In this step the contents of C-array airydisk is copied into a column
|
||||
// of the datastore in row-major order
|
||||
size_t cAiryDisk=ds->addCopiedImageAsColumn(airydisk, NX, NY, "imagedata");
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. create graphs in the plot, which plots the dataset year/other, year/coal, ...
|
||||
// The color of the graphs is set by calling set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(), which sets the
|
||||
// fillColor to the given color and makes the outline of the bars (i.e. their "color") a darker
|
||||
// shade of the given color.
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. create a graph (JKQTPColumnMathImage) with the column created above as data
|
||||
// The data is color-coded with the color-palette JKQTPMathImageMATLAB
|
||||
// the converted range of data is determined automatically because set_autoImageRange(true)
|
||||
JKQTPColumnMathImage* graph=new JKQTPColumnMathImage(&plot);
|
||||
graph->set_title("");
|
||||
// image column with the data
|
||||
graph->set_imageColumn(cAiryDisk);
|
||||
// set size of the data (the datastore does not contain this info, as it only manages 1D columns of data and this is used to assume a row-major ordering
|
||||
graph->set_Nx(NX);
|
||||
graph->set_Ny(NY);
|
||||
// where does the image start in the plot, given in plot-axis-coordinates (bottom-left corner)
|
||||
graph->set_x(-w/2.0);
|
||||
graph->set_y(-h/2.0);
|
||||
// width and height of the image in plot-axis-coordinates
|
||||
graph->set_width(w);
|
||||
graph->set_height(h);
|
||||
graph->set_palette(JKQTPMathImageMATLAB); // color-map is "MATLAB"
|
||||
graph->get_colorBarRightAxis()->set_axisLabel("light intensity [A.U.]"); // get coordinate axis of color-bar and set its label
|
||||
// color-map is "MATLAB"
|
||||
graph->set_palette(JKQTPMathImageMATLAB);
|
||||
// get coordinate axis of color-bar and set its label
|
||||
graph->get_colorBarRightAxis()->set_axisLabel("light intensity [A.U.]");
|
||||
// determine min/max of data automatically and use it to set the range of the color-scale
|
||||
graph->set_autoImageRange(true);
|
||||
// you can set the color-scale range manually by using:
|
||||
// graph->set_autoImageRange(false);
|
||||
// graph->set_imageMin(0);
|
||||
// graph->set_imageMax(10);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 5. add the graphs to the plot, so it is actually displayed
|
||||
plot.addGraph(graph);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 6. set axis labels
|
||||
plot.get_xAxis()->set_axisLabel("x [{\\mu}m]");
|
||||
plot.get_yAxis()->set_axisLabel("y [{\\mu}m]");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 7. fix axis and plot aspect ratio to 1
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_maintainAspectRatio(true);
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_maintainAxisAspectRatio(true);
|
||||
|
||||
116
test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_stackedbars/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
|
||||
[Back to JKQTPlotter main page](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/)
|
||||
|
||||
# JKQtPlotter
|
||||
|
||||
## Simple stacked barchart
|
||||
This project (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_stackedbars/`) simply creates a JKQtPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds several stacked barcharts.
|
||||
|
||||
The soruce code of the main application is (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_stackedbars/jkqtplotter_simpletest_stackedbars.cpp`):
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <QApplication>
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtplotter.h"
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtpbarchartelements.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#define Ndata 5
|
||||
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QApplication app(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore (for convenience)
|
||||
JKQtPlotter plot;
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForGraphs(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForSystem(true); // nicer (but slower) plotting
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_useAntiAliasingForText(true); // nicer (but slower) text rendering
|
||||
JKQTPdatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. now we create data for the charts (taken from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Energiemix_Deutschland.svg)
|
||||
QVector<double> year, percentage_other, percentage_coaloil, percentage_gas, percentage_nuclear, percentage_green;
|
||||
year << 1990 << 1995 << 2000 << 2005 << 2010 << 2015;
|
||||
percentage_other << 3.5 << 3.5 << 4.4 << 4.4 << 5 << 5 ;
|
||||
percentage_coaloil << 58.7 << 55.7 << 51.5 << 48.2 << 42.9 << 43.1;
|
||||
percentage_gas << 6.5 << 7.7 << 8.5 << 11.7 << 14.1 << 9.6 ;
|
||||
percentage_nuclear << 27.7 << 28.7 << 29.4 << 26.2 << 22.2 << 14.2;
|
||||
percentage_green << 3.6 << 4.4 << 6.2 << 9.5 << 15.8 << 28.1;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal datastore.
|
||||
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise)
|
||||
// the variables cYear, cOther ... will contain the internal column ID of the
|
||||
// newly created columns with names "year" and "other" ... and the (copied) data
|
||||
size_t cYear=ds->addCopiedColumn(year, "year");
|
||||
size_t cOther=ds->addCopiedColumn(percentage_other, "other");
|
||||
size_t cCoalOil=ds->addCopiedColumn(percentage_coaloil, "coal & oil");
|
||||
size_t cGas=ds->addCopiedColumn(percentage_gas, "natural gas");
|
||||
size_t cNuclear=ds->addCopiedColumn(percentage_nuclear, "nuclear energy");
|
||||
size_t cGreen=ds->addCopiedColumn(percentage_green, "green energy");
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. create graphs in the plot, which plots the dataset year/other, year/coal, ...
|
||||
// The color of the graphs is set by calling set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(), which sets the
|
||||
// fillColor to the given color and makes the outline of the bars (i.e. their "color") a darker
|
||||
// shade of the given color.
|
||||
QVector<JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph*> graphs;
|
||||
graphs.push_back(new JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph(&plot));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_xColumn(cYear);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_yColumn(cOther);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_title(QObject::tr("other sources"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(QColor("red"));
|
||||
graphs.push_back(new JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph(&plot));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_xColumn(cYear);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_yColumn(cCoalOil);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_title(QObject::tr("coal & oil"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(QColor("darkgrey"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->stackUpon(graphs[graphs.size()-2]);
|
||||
graphs.push_back(new JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph(&plot));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_xColumn(cYear);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_yColumn(cGas);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_title(QObject::tr("natural gas"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(QColor("blue"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->stackUpon(graphs[graphs.size()-2]);
|
||||
graphs.push_back(new JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph(&plot));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_xColumn(cYear);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_yColumn(cNuclear);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_title(QObject::tr("nuclear energy"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(QColor("gold"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->stackUpon(graphs[graphs.size()-2]);
|
||||
graphs.push_back(new JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph(&plot));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_xColumn(cYear);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_yColumn(cGreen);
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_title(QObject::tr("green energy"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->set_fillColor_and_darkenedColor(QColor("darkgreen"));
|
||||
graphs.back()->stackUpon(graphs[graphs.size()-2]);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 5. add the graphs to the plot, so it is actually displayed
|
||||
plot.addGraphs(graphs);
|
||||
|
||||
// 6. set axis labels
|
||||
plot.get_xAxis()->set_axisLabel("year");
|
||||
plot.get_yAxis()->set_axisLabel("fraction of energy production in Germany [%]");
|
||||
|
||||
// 7. finally we move the plot key/legend to the outside, top-right
|
||||
// and lay it out as a single row
|
||||
// NOTE: plot is a descendent of QWidget, which uses an internal object of
|
||||
// type JKQTBasePlotter, which does the actual plotting.
|
||||
// So many properties of the plot are only available in this internal
|
||||
// object, which you can access by plot.get_plotter().
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_keyPosition(JKQTPkeyOutsideTopRight);
|
||||
plot.get_plotter()->set_keyLayout(JKQTPkeyLayoutOneRow);
|
||||
|
||||
// 8 autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
|
||||
plot.zoomToFit();
|
||||
|
||||
// show plotter and make it a decent size
|
||||
plot.show();
|
||||
plot.resize(600,400);
|
||||
|
||||
return app.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
The result looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you use `JKQTPbarHorizontalGraphStacked` instead of `JKQTPbarVerticalStackableGraph`, you'll get a result like this:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Back to JKQTPlotter main page](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/)
|
||||
82
test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_symbols_and_errors/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
|
||||
[Back to JKQTPlotter main page](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/)
|
||||
|
||||
# JKQtPlotter
|
||||
|
||||
## Simple line-graph with error bars
|
||||
This project (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_symbols_and_errors/`) simply creates a JKQtPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds a single line-graph (a sine-wave) that has y-errorbars. In addition, this example shows how to change some of the axis properties and how to use LaTeX markup to format axis labels (can actually be used for all labels in JKQtPlotter). Also, in comparison to the last example, here we initialize the data from C-type arrays (double*), instead of QVector<double> objects.
|
||||
|
||||
The soruce code of the main application is (see `./test/jkqtplotter_simpletest_symbols_and_errors/jkqtplotter_simpletest_symbols_and_errors.cpp`):
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <QApplication>
|
||||
#include "jkqtplotter/jkqtplotter.h"
|
||||
|
||||
// number of datapoints:
|
||||
#define Ndata 10
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QApplication app(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
// 1. create a plotter window and get a pointer to the internal datastore (for convenience)
|
||||
JKQtPlotter plot;
|
||||
JKQTPdatastore* ds=plot.getDatastore();
|
||||
|
||||
// 2. now we create data for a simple plot (a sine curve with lin. increasing errors)
|
||||
double X[Ndata], Y[Ndata], YERROR[Ndata];
|
||||
for (int i=0; i<Ndata; i++) {
|
||||
X[i]=double(i)/double(Ndata)*2.0*M_PI;
|
||||
Y[i]=sin(X[i]);
|
||||
YERROR[i]=0.2+double(i)/double(Ndata)*0.25;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 3. make data available to JKQtPlotter by adding it to the internal datastore.
|
||||
// Note: In this step the data is copied (of not specified otherwise), so you can
|
||||
// reuse X and Y afterwards!
|
||||
// the variables columnX and columnY will contain the internal column ID of the newly
|
||||
// created columns with names "x" and "y" and the (copied) data from X and Y.
|
||||
size_t columnX=ds->addCopiedColumn(X, Ndata, "x");
|
||||
size_t columnY=ds->addCopiedColumn(Y, Ndata, "y");
|
||||
size_t columnYE=ds->addCopiedColumn(YERROR, Ndata, "y-error");
|
||||
|
||||
// 4. create a graph in the plot, which plots the dataset X/Y:
|
||||
JKQTPxyLineErrorGraph* graph1=new JKQTPxyLineErrorGraph(&plot);
|
||||
graph1->set_xColumn(columnX);
|
||||
graph1->set_yColumn(columnY);
|
||||
graph1->set_yErrorColumn(columnYE);
|
||||
graph1->set_symbol(JKQTPfilledStar); // set symbol style
|
||||
graph1->set_yErrorStyle(JKQTPerrorBars); // set error indicator type
|
||||
graph1->set_drawLine(false); // don't draw a line
|
||||
graph1->set_title(QObject::tr("sine graph"));
|
||||
|
||||
// 5. add the graph to the plot, so it is actually displayed
|
||||
plot.addGraph(graph1);
|
||||
|
||||
// 6. hide 0-lines
|
||||
plot.getXAxis()->set_showZeroAxis(false);
|
||||
plot.getYAxis()->set_showZeroAxis(false);
|
||||
|
||||
// 7. set some axis properties (we use LaTeX for nice equation rendering)
|
||||
plot.getXAxis()->set_axisLabel(QObject::tr("x-axis $x$ [mm]"));
|
||||
plot.getYAxis()->set_axisLabel(QObject::tr("\\textbf{\\color{red}{y-axis} $\\left(y=\\sin(x)\\pm(0.2+0.25\\cdot x)\\right)$ [A.U.]}"));
|
||||
plot.getXAxis()->set_labelFont("Arial");
|
||||
plot.getYAxis()->set_labelFont("Times New Roman");
|
||||
plot.getYAxis()->set_labelFontSize(12); // large x-axis label
|
||||
plot.getYAxis()->set_tickLabelFontSize(10); // and larger y-axis tick labels
|
||||
|
||||
// 8. autoscale the plot so the graph is contained
|
||||
plot.zoomToFit();
|
||||
|
||||
// show plotter and make it a decent size
|
||||
plot.show();
|
||||
plot.resize(600,400);
|
||||
|
||||
return app.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
The result looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[Back to JKQTPlotter main page](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/)
|
||||