2019-01-20 23:15:10 +08:00
# Example (JKQTPlotter): Plotting Geometric Objects {#JKQTPlotterGeometricGraphs}
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
- improved: geometric objects now use an adaptive drawing algorithm to represent curves (before e.g. ellipses were always separated into a fixed number of line-segments)
- improved: constructors and access functions for several geometric objects (e.g. more constructors, additional functions to retrieve parameters in diferent forms, iterators for polygons, ...)
- new: all geometric objects can either be drawn as graphic element (i.e. lines are straight line, even on non-linear axes), or as mathematical curve (i.e. on non-linear axes, lines become the appropriate curve representing the linear function, connecting the given start/end-points). The only exceptions are ellipses (and the derived arcs,pies,chords), which are always drawn as mathematical curves
2020-09-04 05:08:52 +08:00
This project shows the capabilities of JKQTPlotter `plot` to also draw geometric elements, like circles, ellipses, rectangles etc.
2019-06-21 04:24:47 +08:00
- improved: geometric objects now use an adaptive drawing algorithm to represent curves (before e.g. ellipses were always separated into a fixed number of line-segments)
- improved: constructors and access functions for several geometric objects (e.g. more constructors, additional functions to retrieve parameters in diferent forms, iterators for polygons, ...)
- new: all geometric objects can either be drawn as graphic element (i.e. lines are straight line, even on non-linear axes), or as mathematical curve (i.e. on non-linear axes, lines become the appropriate curve representing the linear function, connecting the given start/end-points). The only exceptions are ellipses (and the derived arcs,pies,chords), which are always drawn as mathematical curves
2020-09-04 05:08:52 +08:00
The source code of the main application can be found in [`geometric.cpp` ](https://github.com/jkriege2/JKQtPlotter/tree/master/examples/geometric/geometric.cpp ). First a plot is generated and the axis aspect ratio is set to 1, so an accurate plot is generated. Then several geometric graphs are added to the plot-> Here are some examples, you can find more more examples in the source code of the example:
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
2019-01-19 16:40:52 +08:00
```.cpp
2020-08-22 00:31:58 +08:00
// a text element
- improved: geometric objects now use an adaptive drawing algorithm to represent curves (before e.g. ellipses were always separated into a fixed number of line-segments)
- improved: constructors and access functions for several geometric objects (e.g. more constructors, additional functions to retrieve parameters in diferent forms, iterators for polygons, ...)
- new: all geometric objects can either be drawn as graphic element (i.e. lines are straight line, even on non-linear axes), or as mathematical curve (i.e. on non-linear axes, lines become the appropriate curve representing the linear function, connecting the given start/end-points). The only exceptions are ellipses (and the derived arcs,pies,chords), which are always drawn as mathematical curves
2020-09-04 05:08:52 +08:00
plot->addGraph(new JKQTPGeoText(plot, 0.1,0.6, "$x_{1/2}=\\frac{\\sqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}$", 10, QColor("red")));
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
2020-08-22 00:31:58 +08:00
// a single symbol
- improved: geometric objects now use an adaptive drawing algorithm to represent curves (before e.g. ellipses were always separated into a fixed number of line-segments)
- improved: constructors and access functions for several geometric objects (e.g. more constructors, additional functions to retrieve parameters in diferent forms, iterators for polygons, ...)
- new: all geometric objects can either be drawn as graphic element (i.e. lines are straight line, even on non-linear axes), or as mathematical curve (i.e. on non-linear axes, lines become the appropriate curve representing the linear function, connecting the given start/end-points). The only exceptions are ellipses (and the derived arcs,pies,chords), which are always drawn as mathematical curves
2020-09-04 05:08:52 +08:00
plot->addGraph(new JKQTPGeoSymbol(plot, 0.1,0.6, JKQTPCircle, 5, QColor("grey")));
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
2020-08-22 00:31:58 +08:00
// a line
2020-09-26 21:58:58 +08:00
JKQTPGeoLine* l;
plot->addGraph(l=new JKQTPGeoLine(plot, 1, 0.05, 1.9, 0.9));
l->setStyle(QColor("red"), 2));
2020-08-22 00:31:58 +08:00
// an arrow
2020-09-26 21:58:58 +08:00
plot->addGraph(new JKQTPGeoArrow(plot, 0.4, 2.5, 0.4, 2.65, JKQTPArrowAndStop, JKQTPFilledArrow));
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
2020-08-22 00:31:58 +08:00
// a one-sided infinite line with slope dy/dx=0.25/0.2
2020-09-26 21:58:58 +08:00
JKQTPGeoInfiniteLine* infLine=new JKQTPGeoInfiniteLine(plot, 1.7, 0.2, 0.2, 0.25);
infLine->setStyle(QColor("green"), 1.5, Qt::PenStyle::DashLine);
2019-01-26 20:00:40 +08:00
infLine->setTwoSided(false);
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
infLine->setAlpha(0.5);
- improved: geometric objects now use an adaptive drawing algorithm to represent curves (before e.g. ellipses were always separated into a fixed number of line-segments)
- improved: constructors and access functions for several geometric objects (e.g. more constructors, additional functions to retrieve parameters in diferent forms, iterators for polygons, ...)
- new: all geometric objects can either be drawn as graphic element (i.e. lines are straight line, even on non-linear axes), or as mathematical curve (i.e. on non-linear axes, lines become the appropriate curve representing the linear function, connecting the given start/end-points). The only exceptions are ellipses (and the derived arcs,pies,chords), which are always drawn as mathematical curves
2020-09-04 05:08:52 +08:00
plot->addGraph(infLine);
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
2020-08-22 00:31:58 +08:00
// a polyline
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
QVector< QPointF > p;
2020-08-23 19:30:20 +08:00
p< < QPointF ( 2 . 1 , 0 . 0 ) < < QPointF ( 2 . 2 , 0 . 92 ) < < QPointF ( 2 . 6 , 0 . 3 ) < < QPointF ( 2 . 9 , 0 . 9 ) ;
2020-09-26 21:58:58 +08:00
JKQTPGeoPolyLines* poly;
plot->addGraph(poly=new JKQTPGeoPolyLines(plot, p));
poly->setStyleTransparentFill(QColor("darkgreen"), 4, Qt::PenStyle::DashDotLine);
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
2020-08-22 00:31:58 +08:00
// rectangle:
2020-09-26 21:58:58 +08:00
JKQTPGeoRectangle* rec;
plot->addGraph(rec=new JKQTPGeoRectangle(plot, QPointF(0.4,1.3), QPointF(0.9,1.6)));
rec->setStyle(QColor("blue"), 1, Qt::SolidLine, rfill, Qt::SolidPattern);
2020-08-22 00:31:58 +08:00
// a rotated rectangle (rotated by 35 degrees):
2020-09-26 21:58:58 +08:00
plot->addGraph(rec=new JKQTPGeoRectangle(plot, 0.5,1.5,0.8,0.5));
rec->setStyleTransparentFill(QColor("darkblue"), 2, Qt::DashLine);
rec->setAngle(35);
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
2020-08-22 00:31:58 +08:00
// ellipse:
2020-09-26 21:58:58 +08:00
JKQTPGeoEllipse* ell;
plot->addGraph(ell=new JKQTPGeoEllipse(plot, QPointF(0.4,1.3), QPointF(0.9,1.6)));
ell->setStyle(QColor("blue"), 1, Qt::SolidLine, rfill, Qt::SolidPattern);
// a rotated rectangle (rotated by 35 degrees):
plot->addGraph(ell=new JKQTPGeoEllipse(plot, 0.5,1.5,0.8,0.5));
ell->setStyleTransparentFill(QColor("darkblue"), 2, Qt::DashLine);
ell->setAngle(35);
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
2020-08-23 19:30:20 +08:00
2020-08-22 00:31:58 +08:00
// a polygon
2020-09-26 21:58:58 +08:00
JKQTPGeoPolygon* polygongraph=new JKQTPGeoPolygon(plot);
polygongraph->setStyle(QColor("red"), 2, Qt::PenStyle::DashLine, QColor("salmon"), Qt::SolidPattern);
2020-08-23 19:30:20 +08:00
polygongraph->appendPoint(2.1, 0.5);
polygongraph->appendPoint(2.9, 0.9);
polygongraph->appendPoint(2.2, 0.8);
polygongraph->appendPoint(2.8, 0.25);
polygongraph->appendPoint(2.6, 0.6);
polygongraph->setAlpha(0.75);
- improved: geometric objects now use an adaptive drawing algorithm to represent curves (before e.g. ellipses were always separated into a fixed number of line-segments)
- improved: constructors and access functions for several geometric objects (e.g. more constructors, additional functions to retrieve parameters in diferent forms, iterators for polygons, ...)
- new: all geometric objects can either be drawn as graphic element (i.e. lines are straight line, even on non-linear axes), or as mathematical curve (i.e. on non-linear axes, lines become the appropriate curve representing the linear function, connecting the given start/end-points). The only exceptions are ellipses (and the derived arcs,pies,chords), which are always drawn as mathematical curves
2020-09-04 05:08:52 +08:00
plot->addGraph(polygongraph);
2020-08-23 19:30:20 +08:00
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
2020-08-22 00:31:58 +08:00
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
// an arc from an ellipse from -10 degrees to 117 degrees, centered at 2.5,1.5 and full axes of 0.5 and 0.5
2020-09-26 21:58:58 +08:00
plot->addGraph(new JKQTPGeoArc(plot,2.5,1.5,0.5,0.5, -10, 117 ));
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
2020-08-22 00:31:58 +08:00
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
// a pie centered at 2.5,2.5 with ellipse axes 0.9 and 0.9 and from angle 0 degrees to 90 degrees
2020-09-26 21:58:58 +08:00
plot->addGraph(new JKQTPGeoPie(plot,2.5,2.5,0.9,0.9, 0, 90));
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
2020-08-22 00:31:58 +08:00
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
// a chord centered at 2.5,2.5 with ellipse axes 0.9 and 0.9 and from angle 0 degrees to 90 degrees
2020-09-26 21:58:58 +08:00
plot->addGraph(new JKQTPGeoChord(plot,2.5,2.5,0.9,0.9, 0, 90));
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
```
The result of the example combines all these elements and looks like this:
2019-06-21 04:24:47 +08:00
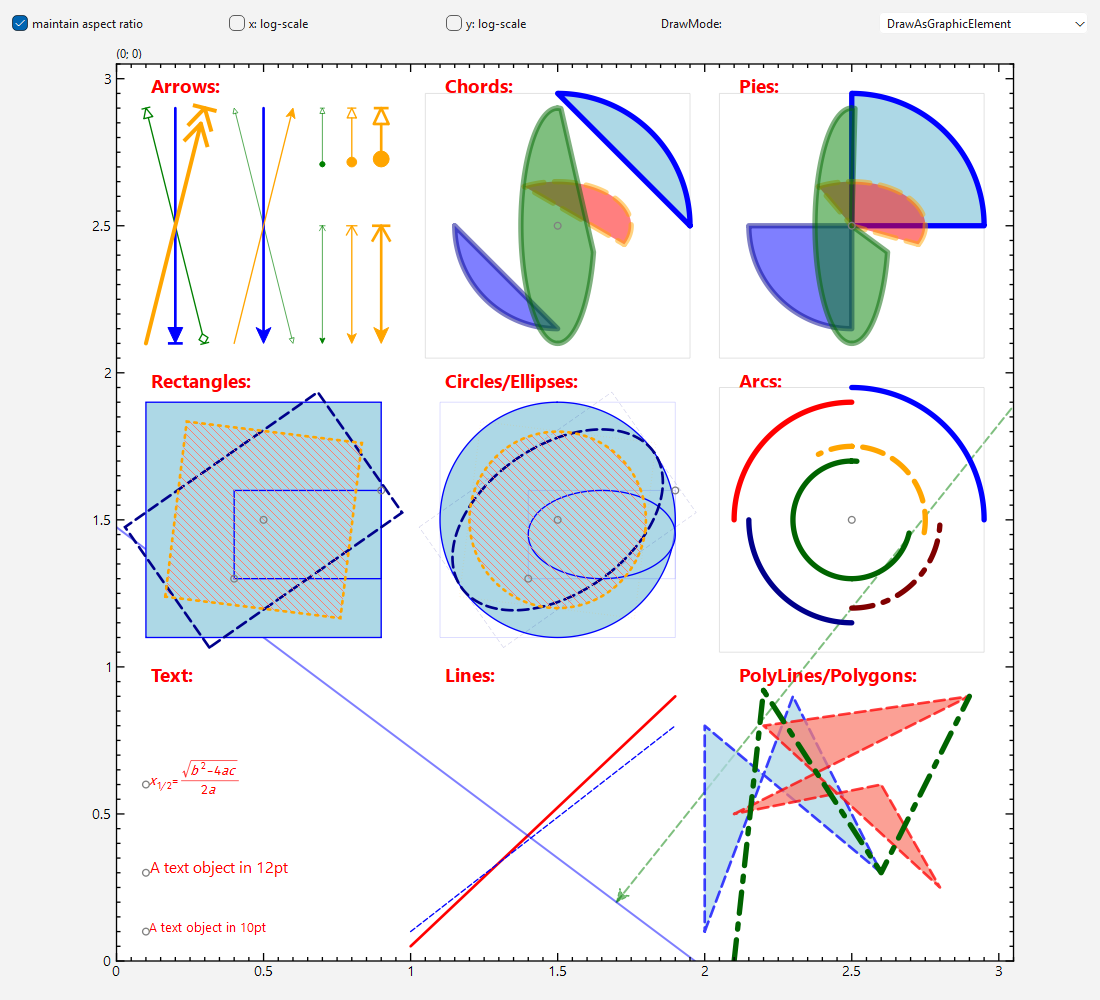
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00
- improved: geometric objects now use an adaptive drawing algorithm to represent curves (before e.g. ellipses were always separated into a fixed number of line-segments)
- improved: constructors and access functions for several geometric objects (e.g. more constructors, additional functions to retrieve parameters in diferent forms, iterators for polygons, ...)
- new: all geometric objects can either be drawn as graphic element (i.e. lines are straight line, even on non-linear axes), or as mathematical curve (i.e. on non-linear axes, lines become the appropriate curve representing the linear function, connecting the given start/end-points). The only exceptions are ellipses (and the derived arcs,pies,chords), which are always drawn as mathematical curves
2020-09-04 05:08:52 +08:00
The example also adds some control-widgets that allow to change the properties of the plot, especially whether the aspect ratio is maintained and whether the axes have logarithmic scaling. This is achieved by code like this:
```.cpp
// 1. create a Widget with a plotter and some control-elements
QWidget widMain;
QGridLayout* layMain=new QGridLayout;
widMain.setLayout(layMain);
JKQTPlotter* plot=new JKQTPlotter(&widMain);
layMain->addWidget(plot, 1,0,1,5);
layMain->setRowStretch(1,1);
QCheckBox* chk;
// when checkbox is toggled: aspect-ration is maintained, or not
layMain->addWidget(chk=new QCheckBox(QObject::tr("maintain aspect ratio"), & widMain), 0, 0);
chk->setChecked(true);
QObject::connect(chk, & QCheckBox::toggled, [plot ](bool checked ) {
plot->getPlotter()->setMaintainAspectRatio(checked);
plot->getPlotter()->setMaintainAxisAspectRatio(checked);
});
// toggling the checkbox switches between linear and log x-axis
layMain->addWidget(chk=new QCheckBox(QObject::tr("x: log-scale"), & widMain), 0, 1);
chk->setChecked(false);
QObject::connect(chk, & QCheckBox::toggled, plot->getPlotter()->getXAxis(), &JKQTPHorizontalAxis::setLogAxis);
// toggling the checkbox switches between linear and log y-axis
layMain->addWidget(chk=new QCheckBox(QObject::tr("y: log-scale"), & widMain), 0, 2);
chk->setChecked(false);
QObject::connect(chk, & QCheckBox::toggled, plot->getPlotter()->getYAxis(), &JKQTPVerticalAxis::setLogAxis);
QComboBox* cmb;
// a combobox to select the DrawMode of all graph elements
layMain->addWidget(new QLabel(QObject::tr("DrawMode: "), & widMain), 0, 3);
layMain->addWidget(cmb=new QComboBox(& widMain), 0, 4);
cmb->addItem(QObject::tr("DrawAsGraphicElement"));
cmb->addItem(QObject::tr("DrawAsMathematicalCurve"));
cmb->setCurrentIndex(0);
QObject::connect(cmb, static_cast< void ( QComboBox:: *)( int ) > (& QComboBox::currentIndexChanged), [plot ](int index ) {
for (size_t i=0; i< plot- > getPlotter()->getGraphCount(); i++) {
2020-09-21 19:15:57 +08:00
JKQTPGeometricPlotElement* obj=dynamic_cast< JKQTPGeometricPlotElement * > (plot->getPlotter()->getGraph(i));
- improved: geometric objects now use an adaptive drawing algorithm to represent curves (before e.g. ellipses were always separated into a fixed number of line-segments)
- improved: constructors and access functions for several geometric objects (e.g. more constructors, additional functions to retrieve parameters in diferent forms, iterators for polygons, ...)
- new: all geometric objects can either be drawn as graphic element (i.e. lines are straight line, even on non-linear axes), or as mathematical curve (i.e. on non-linear axes, lines become the appropriate curve representing the linear function, connecting the given start/end-points). The only exceptions are ellipses (and the derived arcs,pies,chords), which are always drawn as mathematical curves
2020-09-04 05:08:52 +08:00
if (obj) {
2020-09-21 19:15:57 +08:00
obj->setDrawMode((index==0)?JKQTPGeometricPlotElement::DrawAsGraphicElement:JKQTPGeometricPlotElement::DrawAsMathematicalCurve);
- improved: geometric objects now use an adaptive drawing algorithm to represent curves (before e.g. ellipses were always separated into a fixed number of line-segments)
- improved: constructors and access functions for several geometric objects (e.g. more constructors, additional functions to retrieve parameters in diferent forms, iterators for polygons, ...)
- new: all geometric objects can either be drawn as graphic element (i.e. lines are straight line, even on non-linear axes), or as mathematical curve (i.e. on non-linear axes, lines become the appropriate curve representing the linear function, connecting the given start/end-points). The only exceptions are ellipses (and the derived arcs,pies,chords), which are always drawn as mathematical curves
2020-09-04 05:08:52 +08:00
}
}
plot->redrawPlot();
});
```
2020-09-21 19:15:57 +08:00
Now you can play with these controls and see how the different shapes get distorted when these properties change, in dependence of whether the DrawMode is `JKQTPGeometricPlotElement::DrawAsMathematicalCurve` or `JKQTPGeometricPlotElement::DrawAsGraphicElement` .
- improved: geometric objects now use an adaptive drawing algorithm to represent curves (before e.g. ellipses were always separated into a fixed number of line-segments)
- improved: constructors and access functions for several geometric objects (e.g. more constructors, additional functions to retrieve parameters in diferent forms, iterators for polygons, ...)
- new: all geometric objects can either be drawn as graphic element (i.e. lines are straight line, even on non-linear axes), or as mathematical curve (i.e. on non-linear axes, lines become the appropriate curve representing the linear function, connecting the given start/end-points). The only exceptions are ellipses (and the derived arcs,pies,chords), which are always drawn as mathematical curves
2020-09-04 05:08:52 +08:00
2020-09-21 19:15:57 +08:00
Here is an example on log-log axes and DrawMode = `JKQTPGeometricPlotElement::DrawAsGraphicElement` :
- improved: geometric objects now use an adaptive drawing algorithm to represent curves (before e.g. ellipses were always separated into a fixed number of line-segments)
- improved: constructors and access functions for several geometric objects (e.g. more constructors, additional functions to retrieve parameters in diferent forms, iterators for polygons, ...)
- new: all geometric objects can either be drawn as graphic element (i.e. lines are straight line, even on non-linear axes), or as mathematical curve (i.e. on non-linear axes, lines become the appropriate curve representing the linear function, connecting the given start/end-points). The only exceptions are ellipses (and the derived arcs,pies,chords), which are always drawn as mathematical curves
2020-09-04 05:08:52 +08:00
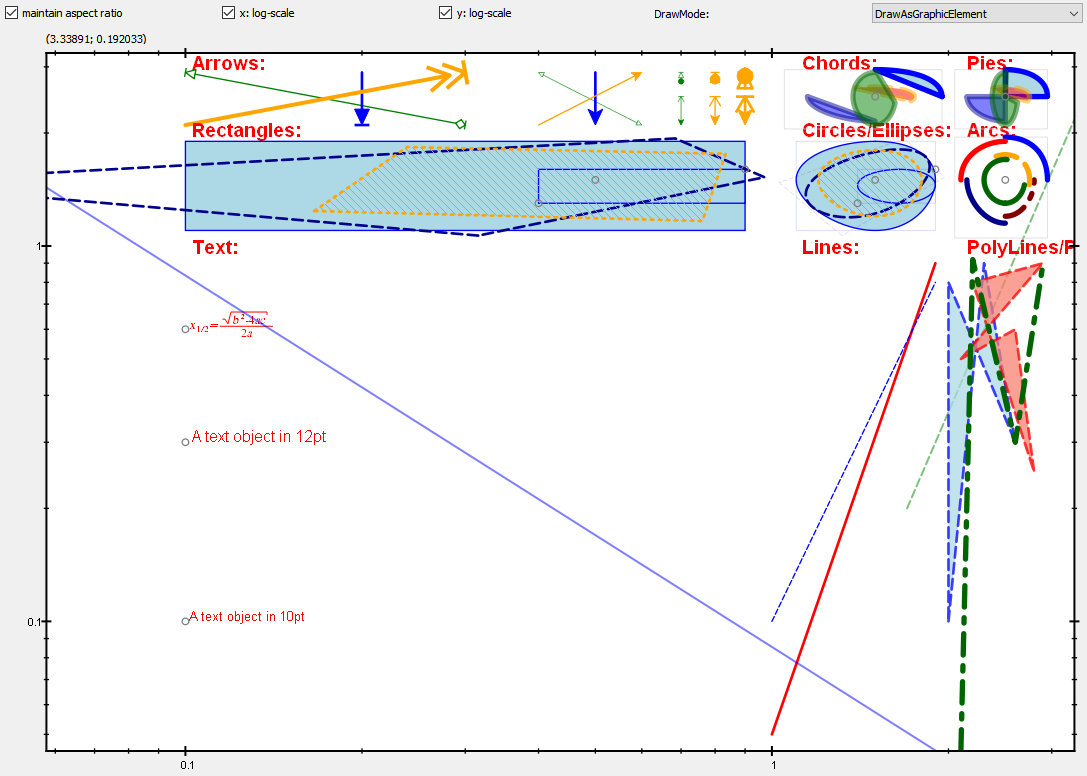
2020-09-21 19:15:57 +08:00
Here is an example on log-log axes and DrawMode = `JKQTPGeometricPlotElement::DrawAsMathematicalCurve` : Observe how straight lines are bent to the appropriate curve!
- improved: geometric objects now use an adaptive drawing algorithm to represent curves (before e.g. ellipses were always separated into a fixed number of line-segments)
- improved: constructors and access functions for several geometric objects (e.g. more constructors, additional functions to retrieve parameters in diferent forms, iterators for polygons, ...)
- new: all geometric objects can either be drawn as graphic element (i.e. lines are straight line, even on non-linear axes), or as mathematical curve (i.e. on non-linear axes, lines become the appropriate curve representing the linear function, connecting the given start/end-points). The only exceptions are ellipses (and the derived arcs,pies,chords), which are always drawn as mathematical curves
2020-09-04 05:08:52 +08:00
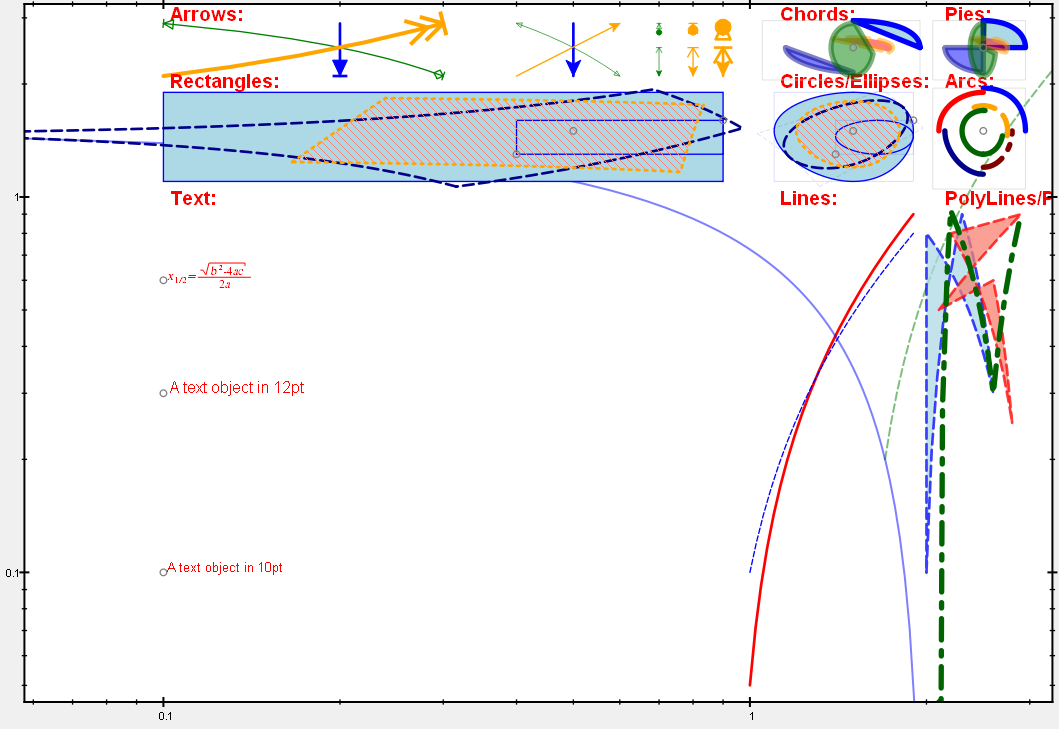
2019-01-08 04:00:56 +08:00